Backwash filters play a crucial role in maintaining efficient water filtration across various industries, from municipal water treatment to industrial processes. These systems are designed to remove accumulated debris and contaminants, ensuring consistent performance and prolonging the lifespan of filtration equipment. While many resources touch on the basics of backwash filters, this article goes a step further, offering deeper insights into their functionality, practical tips for optimization, and expert advice to help you make informed decisions tailored to your specific needs.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Backwash Filters: Definition, Features, and Benefits
What is a Backwash Filter?
A backwash filter is a specialized filtration system designed to remove impurities and debris from water by reversing the flow of water through the filter media. This reverse flow, known as backwashing, dislodges and flushes out accumulated contaminants, restoring the filter’s efficiency without the need for manual cleaning or replacement. Backwash filters are widely used in applications where maintaining consistent water quality is essential, such as municipal water treatment, industrial processes, and irrigation systems.

Key Features and Benefits of Backwash Filters
Backwash filters are equipped with several features that make them a reliable and efficient choice for water filtration. These include automated backwashing mechanisms, durable filter media, and customizable designs to suit specific water treatment needs. One of the standout benefits of these systems is their ability to operate continuously with minimal maintenance, reducing downtime and labor costs. Additionally, backwash filters are highly effective at handling high flow rates and removing a wide range of contaminants, from suspended solids to organic matter.
The benefits extend beyond operational efficiency. By automating the cleaning process, backwash filters help conserve water and reduce waste, making them an environmentally friendly option. Their long lifespan and low maintenance requirements also contribute to cost savings over time, making them a practical choice for both large-scale and small-scale applications.
Backwash Filters vs. Other Filtration Systems
When compared to other filtration systems, such as self-cleaning filters, backwash filters offer unique advantages. While self-cleaning filters rely on mechanisms like rotating brushes or suction scanning to remove debris, backwash filters use the reverse flow of water, which can be more effective for certain types of contaminants. Additionally, backwash filters are often better suited for applications requiring high flow rates and larger volumes of water.
However, self-cleaning filters may be more compact and require less water during the cleaning process, making them ideal for space-constrained environments or applications with limited water availability. The choice between these systems ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as the type of contaminants, flow rate, and operational constraints.
Essential Components of a Backwash Filtration System
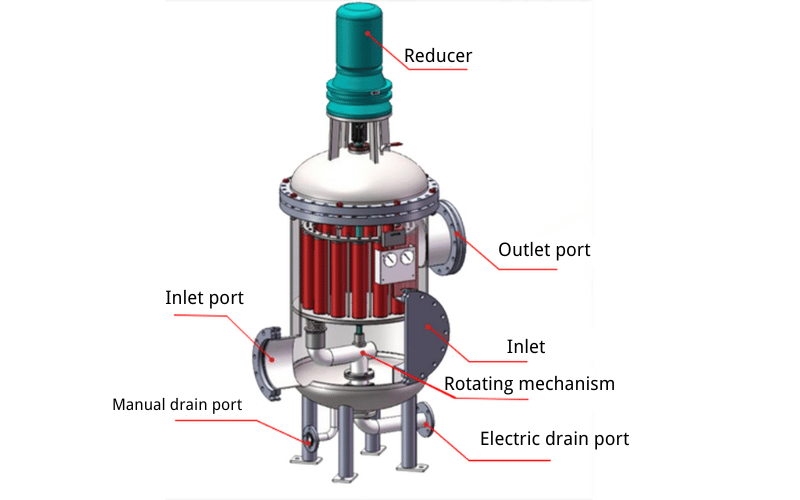
Filter Tank: The Foundation of the System
The filter tank is the primary housing unit where the filtration process takes place. Built from robust materials like fiberglass, stainless steel, or reinforced plastic, the tank is designed to endure high-pressure conditions and long-term use. Inside the tank, the filtration media is layered to trap impurities as water flows through. The size and capacity of the tank are tailored to the specific application, ensuring it can handle varying water volumes and contaminant levels effectively.
Control Valve: The System’s Command Center
The control valve is a critical component that automates the operation of the backwash filter. It regulates the flow of water during both the filtration and backwashing phases, ensuring seamless transitions between cycles. Modern control valves often come with programmable settings, allowing users to adjust backwash frequency and duration based on water quality and system demands. Advanced models may also feature digital interfaces and remote monitoring capabilities, providing greater control and operational efficiency.
Backwash Pump: Powering the Cleaning Process
The backwash pump is responsible for generating the reverse flow of water required to clean the filtration media. By creating sufficient pressure, the pump dislodges trapped debris and flushes it out of the system, restoring the media’s effectiveness. In some systems, the backwash process may rely on existing water pressure instead of a dedicated pump, depending on the design and application requirements.
Filtration Media: The Core of Water Treatment
The filtration media is the material inside the filter tank that captures impurities during the filtration process. Different types of media are used depending on the specific contaminants being targeted. For instance, sand is commonly used for removing suspended solids, while activated carbon is effective for adsorbing organic compounds and chlorine. The choice of media directly impacts the system’s performance and must align with the water treatment goals.
Distribution System: Ensuring Uniform Flow
The distribution system, located at the base of the filter tank, ensures even water flow through the filtration media during both filtration and backwashing. This component typically consists of a network of laterals or a slotted underdrain, designed to prevent media loss while maintaining consistent water distribution. A well-designed distribution system is essential for maximizing filtration efficiency and prolonging the lifespan of the media.
Optional Enhancements: Customizing Performance
Many backwash filtration systems offer optional components to enhance their functionality. Add-ons like pressure gauges and flow meters provide real-time performance data, while air scour systems improve backwashing efficiency by introducing air into the filter bed. These enhancements allow users to tailor their systems to specific operational needs, improving overall performance and efficiency.
How Backwash Filters Operate: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Filtration Process: Capturing Impurities
The operation of a backwash filter begins with the filtration phase, where water flows into the system and passes through the filtration media housed within the filter tank. As the water moves downward:
- Inlet Water Entry: Contaminated water enters the filter tank through the inlet pipe, guided by the control valve.
- Filtration Media Action: The water flows through layers of filtration media, such as sand, anthracite, or activated carbon, which trap suspended solids, organic matter, and other impurities.
- Clean Water Outlet: Once filtered, the clean water exits the system through the outlet pipe, ready for use in industrial, municipal, or other applications.
This process continues until the filtration media becomes saturated with debris, reducing its efficiency and signaling the need for backwashing.
The Backwash Process: Restoring Efficiency
The backwash process is an automated cleaning cycle designed to flush out accumulated contaminants from the filtration media. Here’s how it works step by step:
- Reversing the Flow: The control valve switches the system to backwash mode, reversing the flow of water. Instead of flowing downward, water is directed upward through the filtration media.
- Dislodging Debris: The upward flow agitates the media, loosening trapped particles and debris. This action effectively cleans the media without requiring manual intervention.
- Flushing Out Contaminants: The dislodged impurities are carried away by the backwash water and expelled through a dedicated waste outlet.
- Rinsing and Resetting: After the backwash cycle, a brief rinse cycle may occur to settle the media and remove any remaining debris. The system then resets to filtration mode, ready to resume normal operation.
Automation and Efficiency in Operation
Modern backwash filters are equipped with advanced control valves and sensors that automate the entire process. These systems can be programmed to initiate backwashing based on time intervals, pressure differentials, or water quality parameters. This level of automation ensures consistent performance, reduces maintenance demands, and minimizes water wastage during the cleaning cycle.
Enhancing Understanding with Visuals
To make the operation of backwash filters more engaging and easier to understand, animations or interactive visuals can be highly effective. For example, an animation showing the transition from filtration to backwash mode, with water flow paths and debris removal highlighted, can provide a clear and dynamic explanation of the process. Interactive diagrams that allow users to explore each component and its role in the system can further enhance comprehension, especially for those new to water treatment technologies.
Practical Applications of Backwash Filters Across Industries
Municipal Water Treatment: Ensuring Safe and Clean Water Supply
Backwash filters are a cornerstone of municipal water treatment systems, where they play a critical role in delivering safe and clean drinking water to communities. These filters effectively remove suspended solids, organic matter, and other impurities from raw water sources such as rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. By automating the cleaning process, backwash filters ensure consistent performance and reduce the need for manual maintenance, making them an efficient and reliable solution for large-scale water treatment facilities.
Real-World Example: A municipal water treatment plant in California implemented backwash filters to handle high sediment loads during seasonal changes. The automated backwashing process reduced downtime and improved water clarity, meeting stringent regulatory standards.
Power Plants: Protecting Equipment and Enhancing Efficiency
In power generation facilities, backwash filters are essential for maintaining the quality of cooling water used in turbines and condensers. Contaminants in the water can lead to scaling, corrosion, and reduced efficiency of critical equipment. Backwash filters prevent these issues by removing debris and ensuring a steady supply of clean water, which is vital for uninterrupted power production.
Real-World Example: A thermal power plant in India installed backwash filters to manage the high particulate content in its cooling water. The system’s ability to operate continuously with minimal maintenance significantly reduced operational costs and extended the lifespan of the plant’s equipment.
Food and Beverage Industry: Meeting Stringent Hygiene Standards
The food and beverage sector relies on backwash filters to ensure water used in production processes meets strict hygiene and quality standards. These filters are used to remove impurities from process water, rinse water, and even wastewater, ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Their ability to handle high flow rates and diverse contaminants makes them an ideal choice for this industry.
Real-World Example: A beverage manufacturer in Europe integrated backwash filters into its production line to improve the quality of rinse water used for cleaning bottles. The system’s efficiency reduced water consumption and ensured compliance with food safety standards.
Industrial Manufacturing: Supporting Complex Processes
In industrial manufacturing, backwash filters are used to treat process water and protect sensitive machinery from damage caused by contaminants. Industries such as textiles, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals benefit from these systems, as they ensure consistent water quality and reduce the risk of equipment failure.
Real-World Example: A pharmaceutical company in Japan adopted backwash filters to purify water used in drug formulation. The system’s ability to remove fine particles and organic impurities improved product quality and reduced production downtime.
Irrigation Systems: Enhancing Agricultural Productivity
Backwash filters are widely used in agricultural irrigation systems to prevent clogging of drip lines and sprinklers caused by sediment and organic matter. By ensuring a steady flow of clean water, these filters help maintain the efficiency of irrigation systems and support healthy crop growth.
Real-World Example: A large-scale farm in Australia installed backwash filters to manage sediment-heavy water from a nearby river. The automated system reduced labor costs and improved the performance of the farm’s irrigation network, leading to higher crop yields.
Wastewater Treatment: Promoting Sustainability
In wastewater treatment plants, backwash filters are used to remove suspended solids and other contaminants before water is discharged or reused. Their ability to handle high volumes of water and diverse impurities makes them a key component in sustainable water management practices.
Real-World Example: A wastewater treatment facility in Germany incorporated backwash filters to improve the quality of treated water used for industrial cooling. The system’s efficiency reduced the plant’s environmental footprint and supported its sustainability goals.
Advantages of Backwash Filters: Efficiency, Savings, and Sustainability
Enhanced Water Quality and Prolonged Equipment Lifespan
Backwash filters are designed to deliver consistently high water quality by effectively removing suspended solids, organic matter, and other impurities. This ensures that the treated water meets the required standards for various applications, from industrial processes to municipal water supplies. By maintaining clean water flow, these systems also protect downstream equipment, such as pumps, valves, and heat exchangers, from damage caused by sediment buildup or clogging. This not only extends the lifespan of critical machinery but also reduces the frequency of repairs and replacements, ensuring smoother operations.
Significant Cost Savings Through Automation and Efficiency
One of the standout benefits of backwash filters is their ability to reduce operational costs. Unlike traditional filtration systems that require frequent manual cleaning or replacement of filter media, backwash filters automate the cleaning process, minimizing labor and maintenance expenses. Additionally, their efficient design reduces water and energy consumption during the backwashing cycle, further lowering operational costs. Over time, these savings can add up significantly, making backwash filters a cost-effective solution for both small-scale and large-scale applications.
Positive Environmental Impact Through Resource Conservation
Backwash filters contribute to sustainability by optimizing resource usage. Their automated cleaning process uses less water compared to traditional methods, reducing overall water wastage. Furthermore, by preventing the need for chemical cleaning agents or disposable filter cartridges, these systems minimize environmental pollution. This makes them an eco-friendly choice for industries and municipalities aiming to adopt greener practices and reduce their environmental footprint.
Superior Efficiency Compared to Traditional Filtration Systems
When compared to conventional filtration systems, backwash filters offer several efficiency advantages. Traditional filters often require manual intervention for cleaning or replacement, leading to downtime and higher labor costs. In contrast, backwash filters operate continuously, with automated backwashing ensuring uninterrupted performance. Additionally, their ability to handle high flow rates and diverse contaminants makes them more versatile and reliable in demanding applications. While traditional systems may suffice for smaller or less complex needs, backwash filters are better suited for large-scale operations where efficiency and reliability are critical.
Common Issues with Backwash Filters and How to Troubleshoot Them
Blocked or Clogged Filter Media
One of the most frequent issues with backwash filters is the clogging of filter media due to excessive accumulation of debris and contaminants. This can lead to reduced water flow, decreased filtration efficiency, and increased pressure within the system.
Solution:
- Increase Backwash Frequency: Adjust the control valve settings to initiate backwashing more frequently, especially in systems handling high sediment loads.
- Inspect and Replace Media: Periodically check the condition of the filter media. If it appears worn or compacted, replace it to restore optimal performance.
- Pre-Filtration: Install a pre-filter to capture larger particles before they reach the backwash filter, reducing the load on the media.
Valve Malfunctions
Control valve issues, such as improper switching between filtration and backwash modes, can disrupt the system’s operation. This may be caused by mechanical wear, incorrect programming, or debris obstructing the valve.
Solution:
- Regular Maintenance: Clean the valve components to remove any debris or buildup that may hinder its function.
- Reprogram Settings: Verify that the valve’s settings are correctly programmed for the specific application. Consult the user manual or a technician if needed.
- Replace Faulty Parts: If the valve shows signs of wear or damage, replace the affected components to ensure smooth operation.
Insufficient Backwashing
Inadequate backwashing can result in incomplete cleaning of the filter media, leading to a gradual decline in system efficiency. This issue may arise from low water pressure, incorrect backwash duration, or an undersized backwash pump.
Solution:
- Check Water Pressure: Ensure that the system has adequate water pressure to perform effective backwashing. If necessary, install a booster pump.
- Adjust Backwash Duration: Increase the backwash cycle time to allow thorough cleaning of the media.
- Upgrade Pump Capacity: If the existing pump is insufficient, consider upgrading to a higher-capacity model to improve backwash performance.
Uneven Water Flow Distribution
Uneven water flow through the filter media can lead to channeling, where water bypasses certain areas of the media, reducing filtration efficiency.
Solution:
- Inspect the Distribution System: Check the laterals or underdrain for blockages or damage and clean or replace them as needed.
- Level the Media: Ensure that the filter media is evenly distributed within the tank to promote uniform water flow.
- Air Scour System: Consider adding an air scour system to enhance the backwashing process and prevent channeling.
Leakage or Structural Damage
Leaks in the filter tank, pipes, or connections can compromise the system’s performance and lead to water wastage.
Solution:
- Inspect for Cracks or Loose Fittings: Regularly check the tank, pipes, and connections for signs of wear, cracks, or loose fittings. Tighten or replace components as necessary.
- Use Sealants: Apply appropriate sealants to minor leaks to prevent further damage. For significant structural issues, consult a professional for repairs or replacement.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Performance
- Schedule Regular Inspections: Conduct routine checks of all components, including the filter tank, control valve, and backwash pump, to identify and address potential issues early.
- Clean and Replace Parts as Needed: Keep the system clean and replace worn components, such as filter media and valve seals, to maintain efficiency.
- Monitor System Performance: Use pressure gauges and flow meters to track the system’s performance and identify any deviations from normal operation.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the maintenance recommendations provided by the manufacturer to ensure the system operates as intended.
By addressing these common issues and following proactive maintenance practices, you can maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your backwash filter system.
Maintenance Best Practices for Backwash Filters
Regular Inspections: Identifying Issues Early
Routine inspections are essential to ensure the optimal performance of backwash filters. By regularly checking the system, you can identify potential problems before they escalate into costly repairs or downtime. Key areas to inspect include:
- Filter Media: Look for signs of compaction, wear, or contamination. Replace the media if it appears degraded or no longer effective.
- Control Valve: Check for proper operation and ensure there are no blockages or leaks.
- Pipes and Connections: Inspect for cracks, loose fittings, or signs of leakage that could compromise system efficiency.
- Pressure Gauges and Flow Meters: Monitor these components to detect any deviations in system performance, such as pressure drops or reduced flow rates.
Cleaning Routines: Keeping the System Efficient
Maintaining a clean system is critical for the longevity and efficiency of backwash filters. While the automated backwashing process handles most of the cleaning, additional steps may be necessary:
- Flush the System Periodically: Perform a manual flush to remove any stubborn debris that may not be cleared during regular backwashing cycles.
- Clean the Control Valve: Disassemble and clean the valve components to prevent buildup that could hinder its operation.
- Inspect the Distribution System: Ensure that the laterals or underdrain are free from blockages and functioning correctly.
Tips for Extending the Lifespan of Backwash Filters
To maximize the durability and performance of your backwash filter system, consider the following tips:
- Use High-Quality Filter Media: Invest in durable and effective media that suits your specific water treatment needs. High-quality media lasts longer and provides better filtration.
- Optimize Backwash Settings: Adjust the frequency and duration of backwashing cycles based on water quality and system demands. Over-backwashing can waste water, while under-backwashing can reduce efficiency.
- Install Pre-Filters: Adding a pre-filter can reduce the load on the backwash filter by capturing larger particles, extending the life of the media and other components.
- Protect Against Freezing: In colder climates, ensure the system is insulated or drained during freezing temperatures to prevent damage to the tank and pipes.
Importance of Following Manufacturer Guidelines
Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommendations is crucial for maintaining the performance and reliability of your backwash filter. These guidelines are tailored to the specific design and requirements of your system and typically include:
- Maintenance Schedules: Follow the suggested timelines for inspections, cleaning, and part replacements.
- Replacement Parts: Use manufacturer-approved components to ensure compatibility and maintain warranty coverage.
- Operating Parameters: Stay within the recommended pressure, flow rate, and temperature ranges to avoid overloading the system.
By implementing these maintenance best practices and following the manufacturer’s instructions, you can ensure that your backwash filter operates efficiently, reduces downtime, and delivers consistent water quality over its lifespan.
Innovations in Backwash Filter Technology: Advancing Efficiency and Sustainability
Smart Control Systems: Enhancing Automation and Precision
One of the most significant advancements in backwash filter technology is the integration of smart control systems. These systems use sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity to monitor water quality, pressure, and flow rates in real time. By analyzing this data, smart controls can automatically adjust backwash cycles, ensuring optimal performance while minimizing water and energy usage. Remote monitoring capabilities also allow operators to track system performance and address issues promptly, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
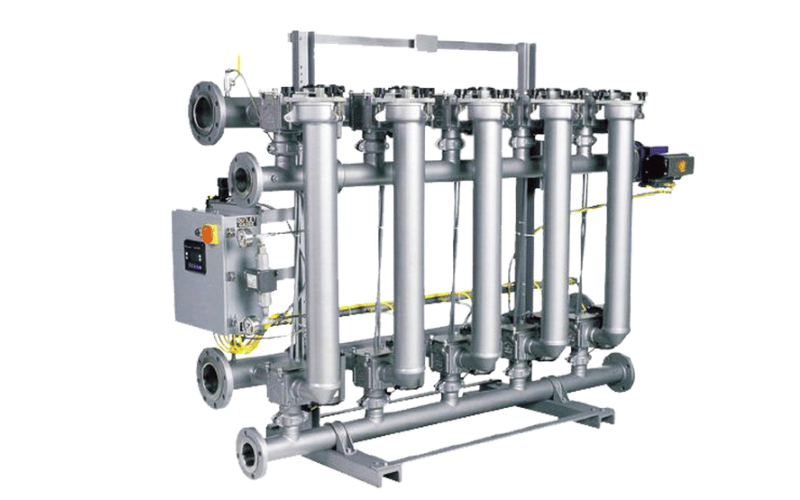

Advanced Filtration Media: Boosting Performance
The development of new filtration media has revolutionized the efficiency of backwash filters. Innovations such as multi-layered media, ceramic beads, and nano-coated materials offer superior contaminant removal and longer lifespans compared to traditional options like sand or anthracite. These advanced media types are designed to handle specific challenges, such as removing microplastics, heavy metals, or oil residues, making them ideal for industries with stringent water quality requirements.
Energy-Efficient Backwashing: Reducing Resource Consumption
Modern backwash filters are increasingly designed with energy efficiency in mind. Innovations such as low-energy pumps and optimized flow dynamics reduce the power required for backwashing, making the process more sustainable. Additionally, some systems now incorporate air scour technology, which uses a combination of air and water to clean the filter media more effectively while using less water overall. These advancements not only lower operational costs but also support environmental conservation efforts.
Modular and Compact Designs: Expanding Applicability
To meet the needs of diverse industries and applications, manufacturers are introducing modular and compact backwash filter designs. Modular systems allow for easy scalability, enabling users to expand their filtration capacity as needed without significant infrastructure changes. Compact designs, on the other hand, are ideal for space-constrained environments, such as urban water treatment facilities or mobile units for remote locations. These innovations make backwash filters more accessible and versatile than ever before.
Sustainable Materials and Eco-Friendly Designs
Sustainability is a growing focus in the development of backwash filter technology. Many manufacturers are now using recyclable or biodegradable materials in their systems to reduce environmental impact. Additionally, eco-friendly designs prioritize water conservation by minimizing waste during the backwashing process. Some systems even incorporate water recovery mechanisms, allowing a portion of the backwash water to be treated and reused, further enhancing sustainability.
AI and Machine Learning: Predictive Maintenance and Optimization
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into backwash filter systems is transforming maintenance and operational efficiency. These technologies analyze historical and real-time data to predict when maintenance is needed, reducing the risk of unexpected failures. AI algorithms can also optimize backwash cycles based on changing water quality conditions, ensuring consistent performance while conserving resources.
Industry-Specific Innovations: Tailored Solutions
Recent advancements have also led to the development of industry-specific backwash filter solutions. For example, filters designed for the food and beverage industry now include features to meet strict hygiene standards, such as stainless steel construction and easy-to-clean components. Similarly, filters for industrial applications are being equipped with enhanced durability to withstand harsh operating conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments.
By embracing these innovations, backwash filter technology continues to evolve, offering improved efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability to meet the growing demands of modern water treatment challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions About Backwash Filters
How Often Should I Backwash My Filter?
The frequency of backwashing depends on several factors, including the quality of the incoming water, the type of filtration media, and the system’s operational demands. In general, most systems require backwashing every few days to a week. However, systems handling high sediment loads or operating in industrial environments may need more frequent cycles. Modern backwash filters equipped with smart control valves can automate this process, initiating backwashing based on pressure differentials or preset intervals.
What Is the Lifespan of a Backwash Filter?
The lifespan of a backwash filter varies depending on its design, materials, and maintenance practices. On average, a well-maintained system can last 10 to 15 years or more. Key components, such as the filter tank and control valve, are built for durability, while parts like the filtration media may need replacement every 3 to 5 years, depending on usage and water quality. Regular inspections and adherence to manufacturer guidelines can significantly extend the system’s lifespan.
Can Backwash Filters Handle High Flow Rates?
Yes, backwash filters are designed to accommodate a wide range of flow rates, making them suitable for both small-scale and large-scale applications. The system’s capacity depends on the size of the filter tank, the type of media used, and the pump’s power. For industries requiring high flow rates, larger or modular systems can be installed to meet the demand without compromising efficiency.
Are Backwash Filters Suitable for All Types of Water?
Backwash filters are versatile and can handle various water types, including municipal, industrial, and agricultural water. However, the choice of filtration media and system configuration should be tailored to the specific contaminants present in the water. For example, sand media is effective for removing suspended solids, while activated carbon is better suited for adsorbing organic compounds and chlorine. Consulting with a water treatment specialist can help determine the best setup for your needs.
How Much Water Is Used During Backwashing?
The amount of water used during backwashing depends on the system’s size and design. On average, backwashing consumes 2% to 5% of the total water processed by the filter. Advanced systems with optimized backwash cycles or air scour technology can reduce water usage, making the process more efficient and environmentally friendly.
What Maintenance Is Required for Backwash Filters?
Routine maintenance is essential to keep backwash filters operating efficiently. Key tasks include inspecting the filter media, cleaning the control valve, checking for leaks, and monitoring system performance using pressure gauges and flow meters. Replacing worn components, such as media or valve seals, as needed will also help maintain optimal performance. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule is critical for long-term reliability.
Can Backwash Filters Be Used in Harsh Environments?
Yes, many backwash filters are designed to withstand challenging conditions, such as high temperatures, corrosive environments, or heavy sediment loads. Systems constructed with durable materials like stainless steel or reinforced fiberglass are particularly suited for industrial and outdoor applications. Additionally, protective coatings and specialized components can be added to enhance durability in extreme environments.
What Are the Advantages of Automated Backwash Filters?
Automated backwash filters offer several benefits, including reduced labor costs, consistent performance, and improved resource efficiency. These systems use programmable control valves to initiate backwashing based on time intervals, pressure changes, or water quality parameters. Automation ensures that the system operates optimally with minimal manual intervention, making it a convenient and cost-effective solution for various applications.
How Do I Choose the Right Backwash Filter for My Needs?
Selecting the right backwash filter involves evaluating factors such as water quality, flow rate, and the specific contaminants to be removed. Consider the system’s capacity, filtration media, and additional features like automation or modularity. Consulting with a water treatment expert or the manufacturer can help you choose a system that meets your operational and budgetary requirements.
Conclusion
Backwash filters are a vital solution for maintaining water quality across various industries, offering benefits such as improved efficiency, reduced maintenance, and sustainability. By understanding their components, operation, and applications, as well as staying informed about innovations and best practices, users can maximize the performance and lifespan of these systems. If you’re considering implementing a backwash filter or upgrading your current setup, explore the available options and consult with water treatment experts to find the best solution for your needs.




