Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a groundbreaking water purification technology that offers an effective solution to combat water contamination. By efficiently removing impurities, RO has become indispensable in both industrial and household settings, ensuring access to clean and safe water. This article delves into the mechanics of RO, its numerous benefits, and its diverse applications across various sectors.
Understanding Reverse Osmosis: A Simple Guide
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that removes impurities and contaminants from water by forcing it through a specialized, semi-permeable membrane. This membrane acts as a barrier, allowing only water molecules to pass through while blocking larger particles, such as salts, bacteria, and other impurities. Essentially, reverse osmosis transforms contaminated or saline water into clean, drinkable water by filtering out unwanted substances.
The Science Behind Reverse Osmosis
To understand reverse osmosis, it helps first to grasp the concept of natural osmosis. Osmosis is a process where water naturally moves from an area of low solute concentration (like freshwater) to an area of high solute concentration (like saltwater) through a semi-permeable membrane. This movement continues until the concentrations on both sides of the membrane equalize.
Reverse osmosis flips this natural process. Instead of water moving toward the higher concentration, external pressure is applied to push water in the opposite direction—from the area of high solute concentration to the area of low solute concentration. This pressure forces water through the semi-permeable membrane, leaving behind contaminants and impurities. The result is purified water on one side and a concentrated solution of impurities on the other.
A Relatable Analogy: The RO Membrane as a Fine Sieve
Think of the reverse osmosis membrane as a super-fine sieve. Imagine trying to strain sand and pebbles from water using a cloth. The cloth allows water to pass through while trapping the sand and pebbles. Similarly, the RO membrane has microscopic pores that are small enough to let water molecules pass but block larger particles like dissolved salts, bacteria, and other impurities. This “sieving” process ensures that the water you get is clean and safe for consumption.
By combining the principles of natural osmosis with applied pressure and advanced filtration technology, reverse osmosis has become one of the most effective methods for water purification. It is widely used in households, industries, and even desalination plants to provide clean water for various purposes.
How Reverse Osmosis Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
The Reverse Osmosis Process Explained
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a multi-stage water purification method that effectively removes impurities, delivering clean and safe water. Each stage of the process plays a critical role in ensuring the water is thoroughly filtered. Below is a detailed breakdown of how reverse osmosis works, step by step.
Step 1: Pre-Filtration to Remove Large Particles
Before water reaches the reverse osmosis membrane, it undergoes pre-filtration to eliminate larger contaminants. This stage typically involves sediment and carbon filters. Sediment filters trap visible particles like dirt, sand, and rust, while carbon filters reduce chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other chemicals that could damage the RO membrane. Pre-filtration not only protects the membrane but also improves the overall efficiency of the system.
For example, imagine cleaning a strainer before using it to filter fine particles. If the strainer is clogged with debris, it won’t work effectively. Similarly, pre-filtration ensures the RO membrane remains unclogged and functional.
Step 2: Applying Pressure to Push Water Through the Membrane
Once pre-filtration is complete, the system applies high pressure to the water. This pressure is essential because it forces water molecules through the semi-permeable membrane, which has incredibly tiny pores. These pores are so small that they block contaminants like dissolved salts, bacteria, and heavy metals while allowing only pure water molecules to pass through.
Think of this step as squeezing juice from a fruit. The pressure ensures that only the liquid (water) is extracted, leaving behind the pulp (contaminants). The amount of pressure required depends on the concentration of impurities in the water. For instance, desalinating seawater requires significantly more pressure than purifying tap water.
Step 3: Separation of Contaminants from Purified Water
As water passes through the membrane, it separates into two streams: purified water and wastewater. The purified water, free from impurities, flows into a storage tank or directly to the faucet for use. Meanwhile, the wastewater, containing the concentrated contaminants, is flushed out of the system.
This separation process ensures that the purified water is of high quality, suitable for drinking, cooking, or other applications. The wastewater, though discarded, plays a vital role in carrying away the impurities, preventing them from accumulating in the system.
Visualizing the Reverse Osmosis Process
To better understand the reverse osmosis process, the following diagram shows the various stages:
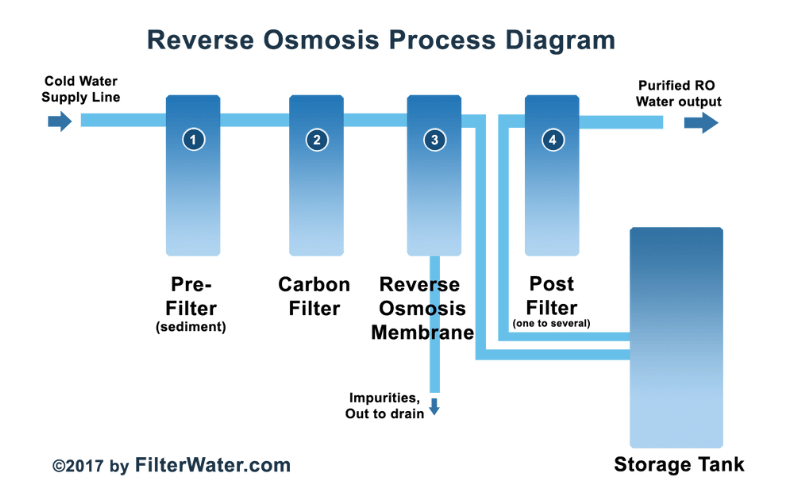
- Pre-Filtration: Water enters the system and passes through sediment and carbon filters.
- Pressure Application: High pressure pushes water through the semi-permeable membrane.
- Separation: Purified water is collected, and wastewater is expelled.
This visual representation simplifies the complex process, making it easier to grasp how reverse osmosis transforms contaminated water into clean, usable water.
Key Components of a Reverse Osmosis System
Understanding the Essential Parts of an RO System
A reverse osmosis (RO) system consists of several critical components, each playing a distinct role in the water purification process. Together, these parts ensure the system effectively removes impurities and delivers clean, safe water. Below is a detailed explanation of the main components and their functions.
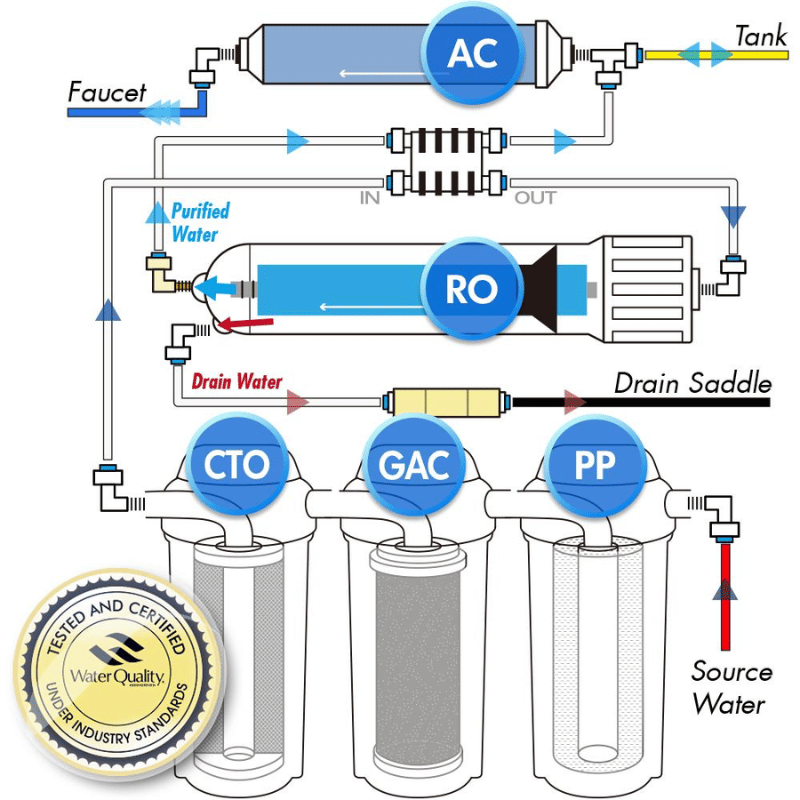
Pre-Filters: The First Line of Defense
Pre-filters are the initial stage in an RO system, designed to protect the delicate RO membrane by removing larger particles and harmful chemicals. These filters typically include:
- Sediment Filters: These filters trap visible particles like dirt, sand, and rust that could clog the system. By removing these larger contaminants, sediment filters prevent damage to the RO membrane and improve the system’s efficiency.
- Carbon Filters: Carbon filters target chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other chemicals that can degrade the RO membrane. Chlorine, in particular, is highly damaging to the membrane, so its removal is crucial for the system’s longevity.
Think of pre-filters as the gatekeepers of the system, ensuring that only pre-treated water reaches the more sensitive components.
The RO Membrane: The Heart of the System
The reverse osmosis membrane is the core component of the system, responsible for the actual purification process. This semi-permeable membrane has microscopic pores that allow only water molecules to pass through while blocking dissolved salts, heavy metals, bacteria, and other impurities.
For example, the RO membrane can remove contaminants as small as 0.0001 microns, making it highly effective at filtering out even the tiniest pollutants. Without this critical component, the system would not be able to produce water of such high purity.
Post-Filters: Polishing the Water
After water passes through the RO membrane, it flows through post-filters, which act as a final polishing stage. These filters enhance the taste and quality of the purified water by removing any remaining odors or minor impurities.
- Polishing Filters: Often made of activated carbon, these filters ensure the water tastes fresh and clean. They are particularly useful for removing any residual chemicals or odors that may have been missed in earlier stages.
Post-filters ensure that the water delivered to your faucet is not only safe but also pleasant to drink.
Storage Tank and Faucet: Delivering Purified Water
Once the water has been purified, it is stored in a pressurized storage tank until needed. The tank ensures a steady supply of clean water, even during high-demand periods. When you turn on the faucet, the purified water flows directly from the storage tank to your glass or sink.
- Storage Tank: This component holds the purified water, keeping it ready for use. The tank is typically equipped with a bladder that maintains pressure, ensuring a consistent flow of water.
- Faucet: The dedicated faucet is the final point of delivery, designed to dispense the purified water. Many RO systems include a separate faucet to prevent cross-contamination with unfiltered water.
Together, the storage tank and faucet make the purified water easily accessible, completing the system’s functionality.
How These Components Work Together
Each component in an RO system plays a vital role in the purification process. Pre-filters prepare the water, the RO membrane performs the heavy lifting by removing contaminants, post-filters polish the water for taste and quality, and the storage tank and faucet ensure convenient access. This seamless integration of parts ensures the system delivers water that is not only clean but also enjoyable to drink.
Advantages of Reverse Osmosis: Why It’s a Top Choice for Water Purification
Removes Up to 99% of Contaminants
One of the most significant benefits of reverse osmosis is its ability to remove up to 99% of impurities from water. The semi-permeable membrane in an RO system effectively filters out a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved salts, heavy metals like lead and mercury, harmful bacteria, and even microscopic particles. This high level of filtration ensures that the water you consume is not only safe but also free from potentially harmful substances.
For instance, reverse osmosis can eliminate contaminants that are often missed by other filtration methods, such as fluoride and nitrates. This makes it an excellent choice for households and industries that require exceptionally pure water for drinking, cooking, or specialized applications.
Improves Taste and Odor of Water
Beyond removing harmful impurities, reverse osmosis significantly enhances the taste and smell of water. Many contaminants, such as chlorine, sulfur, and dissolved minerals, can give water an unpleasant taste or odor. By filtering out these substances, RO systems deliver water that is crisp, clean, and refreshing.
Imagine drinking water that tastes as pure as bottled water but comes straight from your tap. This improvement in taste and odor makes reverse osmosis a popular choice for households, especially in areas where tap water has a noticeable chemical or metallic flavor.
Energy-Efficient Compared to Other Purification Methods
Reverse osmosis is surprisingly energy-efficient, especially when compared to other advanced water purification methods like distillation. While distillation requires significant energy to boil and condense water, RO systems rely on pressure to push water through the membrane, consuming far less energy in the process.
This efficiency makes reverse osmosis an environmentally friendly option for water purification. It provides high-quality results without the excessive energy consumption associated with other methods, making it both cost-effective and sustainable for long-term use.
Versatile Applications for Various Needs
The versatility of reverse osmosis extends beyond just providing clean drinking water. RO systems are widely used in a variety of applications, including:
- Residential Use: Ensures safe and great-tasting water for drinking, cooking, and even ice-making.
- Industrial Applications: Provides ultra-pure water for manufacturing processes, pharmaceuticals, and electronics production.
- Desalination: Converts seawater into potable water, making it a vital technology in regions with limited freshwater resources.
- Agriculture: Supplies purified water for irrigation, improving crop quality and yield.
This adaptability makes reverse osmosis a valuable solution for both personal and professional needs, catering to a wide range of water purification requirements.
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Reverse Osmosis
Despite its many advantages, reverse osmosis is sometimes criticized for “wasting water.” While it’s true that RO systems produce wastewater during the filtration process, modern systems have become much more efficient. Many now feature water-saving technologies that reduce the amount of wastewater generated, making them more eco-friendly than ever before.
Additionally, some people believe that reverse osmosis removes beneficial minerals from water. While it does filter out minerals, most of these are inorganic and not easily absorbed by the body. The primary source of essential minerals should come from a balanced diet, not drinking water. For those concerned, remineralization filters can be added to RO systems to reintroduce healthy minerals like calcium and magnesium.
By addressing these misconceptions, it becomes clear that reverse osmosis remains one of the most effective and practical methods for water purification, offering unmatched benefits for households, industries, and the environment.
What Contaminants Does Reverse Osmosis Remove?
A Comprehensive Look at Impurities Removed by Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is renowned for its ability to remove a wide range of contaminants, making it one of the most effective water purification methods available. The semi-permeable membrane in an RO system acts as a powerful barrier, filtering out impurities that can affect water quality, safety, and taste. Below is a detailed breakdown of the contaminants that reverse osmosis effectively eliminates.
Heavy Metals
Reverse osmosis is highly effective at removing heavy metals, which can pose serious health risks when consumed over time. These metals often enter water supplies through industrial waste, corroded pipes, or natural deposits. RO systems can filter out:
- Lead: A toxic metal that can cause developmental issues in children and kidney damage in adults.
- Mercury: Known for its harmful effects on the nervous system.
- Arsenic: A carcinogenic contaminant often found in groundwater.
- Cadmium: Linked to kidney damage and bone disorders.
By removing these heavy metals, reverse osmosis ensures that the water you consume is safe and free from harmful toxins.
Salts and Dissolved Solids
RO systems excel at reducing total dissolved solids (TDS), which include salts and minerals that can make water taste salty or metallic. These systems can remove:
- Sodium: Common in areas with hard water or seawater intrusion.
- Chloride: Often found in high concentrations in brackish or saline water.
- Calcium and Magnesium: While these minerals are not harmful, they contribute to water hardness, which can cause scaling in pipes and appliances.
By reducing TDS, reverse osmosis improves the taste and usability of water, making it ideal for drinking and cooking.
Nitrates and Nitrites
Nitrates and nitrites, commonly found in agricultural runoff and fertilizers, can contaminate water supplies and pose health risks, especially to infants. Reverse osmosis effectively removes these compounds, ensuring water is safe for consumption.
Fluoride
Fluoride, often added to municipal water supplies to promote dental health, can be harmful in excessive amounts. Reverse osmosis removes fluoride, providing an option for those who prefer fluoride-free water or live in areas with naturally high fluoride levels.
Microorganisms and Pathogens
While reverse osmosis is not primarily designed to kill bacteria and viruses, its membrane can block many microorganisms due to its tiny pore size. This includes:
- Bacteria: Such as E. coli and Salmonella.
- Protozoa: Like Giardia and Cryptosporidium.
- Viruses: Though less effective against viruses, RO systems can still reduce their presence significantly.
For added protection, many RO systems include UV sterilizers or additional filters to ensure complete microbial safety.
Chemical Contaminants
Reverse osmosis also removes a variety of chemical pollutants, including:
- Pesticides and Herbicides: Common in agricultural runoff.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Found in industrial waste and household chemicals.
- Chlorine and Chloramines: Often used in water treatment but can affect taste and odor.
Removal Percentages for Common Contaminants
The table below provides an overview of the removal efficiency of reverse osmosis for various contaminants:
| Contaminant | Removal Percentage |
|---|---|
| Lead | 95-99% |
| Arsenic | 92-96% |
| Fluoride | 85-92% |
| Nitrates/Nitrites | 90-95% |
| Sodium | 94-98% |
| Chlorine | 98-99% |
| Total Dissolved Solids | 95-99% |
| Bacteria and Protozoa | 99% |
| Pesticides/Herbicides | 97-99% |
This table highlights the impressive capabilities of reverse osmosis in removing a wide range of impurities, ensuring that the water you consume is not only clean but also safe for your health.
Applications of Reverse Osmosis: Transforming Water Across Industries
Residential Use: Clean and Safe Drinking Water
Reverse osmosis has become a household staple for providing clean, safe, and great-tasting water. Home RO systems are designed to remove impurities like chlorine, lead, fluoride, and other contaminants that can affect water quality and safety. These systems are particularly beneficial in areas where tap water contains high levels of dissolved solids or harmful chemicals.
For example, many families use reverse osmosis systems to ensure their drinking water is free from pollutants, making it safer for children and adults alike. Additionally, RO systems improve the taste of water, which enhances the flavor of beverages like coffee and tea, as well as meals prepared with purified water. Some advanced systems even include remineralization filters to add back essential minerals, ensuring the water is both pure and healthy.
Industrial Applications: Supporting Manufacturing and Power Generation
In the industrial sector, reverse osmosis plays a critical role in processes that require ultra-pure water. Industries such as manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and power generation rely on RO systems to meet stringent water quality standards. These systems help remove dissolved salts, minerals, and other impurities that could interfere with production processes or damage equipment.
- Manufacturing: Industries like electronics and automotive manufacturing use RO water to prevent scaling and corrosion in machinery. High-purity water is essential for processes like rinsing, cooling, and chemical mixing.
- Pharmaceuticals: The pharmaceutical industry depends on reverse osmosis to produce water that meets strict regulatory standards for drug formulation and equipment sterilization.
- Power Plants: In power generation, RO systems provide demineralized water for boilers and cooling systems, ensuring efficient operation and reducing maintenance costs.
By delivering consistent water quality, reverse osmosis enhances productivity and reduces operational risks in these industries.
Food and Beverage Industry: Enhancing Product Quality
The food and beverage sector relies heavily on reverse osmosis for both ingredient water and product concentration. RO systems ensure that water used in food production is free from contaminants that could alter taste, texture, or safety. This is especially important for products like bottled water, soft drinks, and baby formula, where water quality directly impacts the final product.
- Ingredient Water: Reverse osmosis provides purified water for mixing, cooking, and cleaning, ensuring that food and beverages meet high safety and quality standards.
- Product Concentration: In processes like juice concentration or dairy production, RO systems remove excess water while retaining essential nutrients and flavors. This method is more energy-efficient than traditional evaporation techniques, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
By improving water quality and optimizing production processes, reverse osmosis helps the food and beverage industry deliver superior products to consumers.
Environmental Applications: Desalination and Wastewater Treatment
Reverse osmosis plays a vital role in addressing global water challenges, particularly in desalination and wastewater treatment. These applications are crucial for providing clean water in regions with limited freshwater resources and for reducing environmental pollution.
- Desalination: RO systems are widely used to convert seawater into potable water, making them a lifeline for arid regions and coastal communities. By removing salts and other impurities, reverse osmosis provides a sustainable solution to water scarcity.
- Wastewater Treatment: Industries and municipalities use reverse osmosis to treat wastewater, removing contaminants before discharging it into the environment or reusing it for non-potable purposes. This process helps reduce pollution and conserve water resources.
These environmental applications highlight the versatility of reverse osmosis in tackling some of the most pressing water-related issues of our time. By providing innovative solutions for desalination and wastewater management, RO technology contributes to a more sustainable future.
Challenges and Limitations of Reverse Osmosis: Addressing the Drawbacks
Inability to Remove Certain Microorganisms Without Pre-Treatment
While reverse osmosis is highly effective at removing a wide range of contaminants, it has limitations when it comes to certain microorganisms, particularly smaller viruses and some bacteria. The semi-permeable membrane in an RO system has pores small enough to block most bacteria and protozoa, but it may not completely eliminate all viruses due to their smaller size. This limitation can pose a risk in areas where water sources are heavily contaminated with pathogens.
To address this challenge, many RO systems incorporate pre-treatment methods such as UV sterilization or chlorination. These additional steps ensure that harmful microorganisms are neutralized before the water reaches the RO membrane. By combining reverse osmosis with effective pre-treatment, users can achieve a higher level of water safety and quality.
Maintenance Requirements: Keeping the System in Optimal Condition
Reverse osmosis systems require regular maintenance to function effectively, which can be a drawback for some users. Over time, the RO membrane and filters can become clogged with impurities, reducing the system’s efficiency and water output. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Membrane Cleaning: Mineral scaling and biofouling can accumulate on the membrane, necessitating periodic cleaning to restore its performance.
- Filter Replacement: Pre-filters and post-filters need to be replaced regularly to prevent clogging and ensure optimal water quality.
Neglecting these maintenance tasks can lead to reduced system efficiency, higher energy consumption, and even damage to the membrane. To overcome this challenge, users should follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and invest in high-quality replacement parts. Many modern RO systems also feature indicators or alerts to notify users when maintenance is required, simplifying the process.
Wastewater Generation: A Common Concern
One of the most frequently cited drawbacks of reverse osmosis is the generation of wastewater during the filtration process. For every gallon of purified water produced, traditional RO systems can waste two to three gallons of water, which is expelled as brine. This inefficiency can be a concern in regions facing water scarcity or for environmentally conscious users.
To mitigate this issue, manufacturers have developed water-saving technologies that significantly reduce wastewater production. For example:
- High-Efficiency RO Systems: These systems use advanced membranes and pressure recovery technologies to minimize water waste, achieving recovery rates of up to 80%.
- Recycling Wastewater: Some systems allow users to collect and reuse the wastewater for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation or cleaning.
- Dual-Pass RO Systems: In industrial applications, dual-pass systems treat the wastewater a second time to extract additional purified water, further reducing waste.
By adopting these solutions, users can minimize the environmental impact of reverse osmosis while still enjoying its benefits.
Balancing Challenges with Practical Solutions
While reverse osmosis has its limitations, these challenges can be effectively managed with the right strategies. Pre-treatment methods address the issue of microorganism removal, regular maintenance ensures system efficiency, and water-saving technologies reduce wastewater generation. By understanding and addressing these drawbacks, users can maximize the benefits of reverse osmosis and enjoy clean, safe water with minimal inconvenience.
Why Pre-Filtration is Crucial for Reverse Osmosis Systems
Protecting the RO Membrane: The Primary Role of Pre-Filters
Pre-filtration serves as the first line of defense in a reverse osmosis system, ensuring that the delicate RO membrane remains protected from damage and clogging. The RO membrane is designed to filter out microscopic impurities, but it is highly sensitive to larger particles, chemicals, and sediments that can reduce its efficiency or even cause irreversible damage. Without pre-filters, contaminants like dirt, rust, chlorine, and organic compounds can accumulate on the membrane, leading to scaling, fouling, and a shorter lifespan.
By removing these larger impurities before water reaches the RO membrane, pre-filters not only safeguard the membrane but also enhance the overall performance of the system. This protection ensures that the membrane can focus on filtering out dissolved salts, heavy metals, and other microscopic contaminants, delivering high-quality purified water.
Common Pre-Filtration Methods: Sediment and Carbon Filters
Pre-filtration typically involves a combination of sediment and activated carbon filters, each designed to target specific types of contaminants. These filters work together to prepare the water for the reverse osmosis process, ensuring optimal system performance.
- Sediment Filters: These filters trap visible particles like sand, dirt, rust, and other debris that can clog the RO membrane. Sediment filters are especially important in areas with hard water or older plumbing systems, where particulate matter is more common. By removing these larger particles, sediment filters prevent blockages and reduce wear and tear on the system.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Carbon filters target chemical contaminants, such as chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and pesticides, that can damage the RO membrane or affect the taste and odor of the water. Chlorine, in particular, is highly corrosive to the membrane and must be removed during pre-filtration. Activated carbon filters use adsorption to trap these chemicals, ensuring that the water entering the RO membrane is free from harmful substances.
Together, these pre-filtration methods create a multi-layered barrier that protects the RO system and improves the quality of the purified water.
Cost and Efficiency Benefits of Proper Pre-Filtration
Investing in effective pre-filtration not only protects the RO membrane but also delivers significant cost and efficiency benefits. By reducing the load on the membrane, pre-filters extend its lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacements and lowering maintenance costs. Membranes are one of the most expensive components of an RO system, so prolonging their usability can result in substantial savings over time.
Additionally, proper pre-filtration improves the overall efficiency of the system. When the RO membrane is free from clogs and fouling, it can operate at peak performance, producing purified water more quickly and with less energy consumption. This efficiency translates to lower operating costs and a more sustainable water purification process.
For example, a well-maintained pre-filtration system can reduce the risk of downtime caused by membrane failure, ensuring uninterrupted access to clean water. It also minimizes the need for frequent cleaning or chemical treatments, further reducing maintenance expenses and environmental impact.
The Bottom Line: Pre-Filtration as a Key to Longevity and Performance
Pre-filtration is an essential component of any reverse osmosis system, playing a critical role in protecting the RO membrane, enhancing system efficiency, and reducing long-term costs. By incorporating high-quality sediment and activated carbon filters, users can ensure that their RO system operates smoothly and delivers consistently pure water. Proper pre-filtration is not just a precaution—it is a vital step in maximizing the performance and lifespan of reverse osmosis systems.
How to Maintain and Clean a Reverse Osmosis System
Step-by-Step Guide to Maintaining Your RO System
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure that your reverse osmosis system operates efficiently and delivers high-quality purified water. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced performance, higher energy consumption, and even damage to the system. Below is a detailed guide to help you maintain and clean your RO system effectively.
Regular Filter and Membrane Replacement
The filters and membrane in an RO system are its most critical components, and they require periodic replacement to maintain optimal performance. Each filter has a specific lifespan, depending on the water quality and usage. Here’s a breakdown of when to replace each component:
- Pre-Filters (Sediment and Carbon Filters): Replace these filters every 6 to 12 months. Pre-filters protect the RO membrane by removing larger particles and chlorine, so keeping them in good condition is crucial.
- RO Membrane: Replace the membrane every 2 to 3 years, depending on the water quality and system usage. If you notice a decline in water output or quality, it may be time to replace the membrane sooner.
- Post-Filters (Polishing Filters): Replace post-filters every 12 months to ensure the purified water remains fresh and free from any residual odors or tastes.
Regularly replacing these components not only ensures the system’s efficiency but also extends its overall lifespan.
Cleaning Methods: Physical and Chemical Approaches
Over time, the RO system can accumulate mineral scaling, biofouling, and other deposits that reduce its performance. Cleaning the system periodically helps restore its efficiency. Here are the two main cleaning methods:
Physical Cleaning
Physical cleaning involves flushing the system to remove debris and sediment buildup. Most RO systems have a flush valve or cleaning mode that allows you to rinse the membrane and filters with water. This process helps dislodge particles and prevent clogging.
- Steps for Physical Cleaning:
- Turn off the water supply and drain the storage tank.
- Open the flush valve or activate the cleaning mode.
- Allow the system to flush for 5 to 10 minutes.
- Close the valve and resume normal operation.
Chemical Cleaning
Chemical cleaning is necessary when mineral scaling or biofouling becomes severe. This process involves using specialized cleaning solutions to dissolve deposits and sanitize the system.
- Steps for Chemical Cleaning:
- Turn off the water supply and disconnect the system.
- Prepare a cleaning solution based on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Circulate the solution through the system using a pump or manually.
- Rinse the system thoroughly with clean water to remove any residual chemicals.
- Reconnect the system and test the water quality before use.
Always use cleaning solutions that are compatible with your RO system to avoid damaging the membrane or other components.
Tips for Extending the Lifespan of Your RO System
Proper care and preventive measures can significantly extend the lifespan of your reverse osmosis system. Here are some practical tips:
- Monitor Water Quality: Test your water regularly to identify changes in quality that may indicate the need for maintenance or filter replacement.
- Install a Water Softener: If you have hard water, consider installing a water softener before the RO system. This reduces mineral scaling and prolongs the life of the membrane.
- Flush the System Regularly: Use the flush valve to rinse the membrane and filters periodically, especially in areas with high TDS (total dissolved solids) levels.
- Check for Leaks: Inspect the system for leaks or loose connections during routine maintenance. Addressing these issues promptly prevents water waste and potential damage.
- Follow the Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Always adhere to the maintenance schedule and cleaning instructions provided by the manufacturer. Using compatible replacement parts and cleaning solutions ensures the system operates as intended.
By following these maintenance and cleaning practices, you can keep your reverse osmosis system running efficiently, reduce the risk of breakdowns, and enjoy consistently high-quality water for years to come.
How to Choose the Right Reverse Osmosis System
Factors to Consider When Selecting an RO System
Choosing the right reverse osmosis system requires careful consideration of your specific needs and circumstances. With various models and features available, understanding the key factors can help you make an informed decision. Below, we explore the most important aspects to evaluate when selecting an RO system.
Water Quality and Source
The quality and source of your water play a significant role in determining the type of RO system you need. Different water sources, such as municipal water, well water, or brackish water, contain varying levels of contaminants. For example:
- Municipal Water: Typically treated with chlorine, municipal water may require an RO system with effective carbon pre-filters to remove chlorine and improve taste.
- Well Water: Often contains higher levels of sediment, iron, and bacteria, making it essential to choose a system with robust pre-filtration and possibly UV sterilization.
- Brackish or Saline Water: Requires a high-pressure RO system designed to handle elevated levels of dissolved salts and minerals.
Testing your water quality before purchasing an RO system can help you identify the specific contaminants present, ensuring you select a system that effectively addresses your needs.
Daily Water Consumption
Your household or business’s daily water consumption is another critical factor to consider. RO systems come in various capacities, and choosing one that matches your usage ensures a steady supply of purified water without overburdening the system.
- Small Households: A compact under-sink RO system with a daily capacity of 50–75 gallons is usually sufficient for a family of two to four people.
- Larger Families or Businesses: For higher water demands, consider a system with a larger storage tank or a higher production rate, such as 100–300 gallons per day.
- Commercial Applications: Businesses like restaurants or manufacturing facilities may require industrial-grade RO systems capable of producing thousands of gallons per day.
By estimating your daily water needs, you can avoid under- or over-investing in a system that doesn’t align with your consumption patterns.
Space and Budget Constraints
The available space in your home or facility and your budget are practical considerations that can influence your choice of an RO system.
- Space Requirements: Under-sink RO systems are compact and ideal for homes with limited space. If space is not a concern, a whole-house RO system can provide purified water to every tap in your home.
- Budget: RO systems vary widely in price, from affordable under-sink models to more expensive whole-house or industrial systems. While higher-end systems may offer advanced features like remineralization or smart monitoring, basic models can still provide excellent water purification at a lower cost.
Balancing your space and budget constraints with your water quality and consumption needs ensures you select a system that fits seamlessly into your lifestyle.
Comparison of Different RO Systems
To help you make an informed decision, here’s a comparison table highlighting the features of various types of RO systems:
| System Type | Best For | Capacity | Key Features | Approx. Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Under-Sink RO | Small households | 50–75 GPD | Compact, easy installation, affordable | $150–$500 |
| Countertop RO | Renters or small spaces | 50–75 GPD | Portable, no permanent installation | $100–$300 |
| Whole-House RO | Large families or entire homes | 500–1,000+ GPD | Purifies water for all taps, high capacity | $1,000–$5,000+ |
| Commercial RO | Businesses and industries | 1,000–10,000+ GPD | High output, customizable configurations | $5,000–$20,000+ |
Making the Right Choice
Selecting the right reverse osmosis system involves evaluating your water quality, daily usage, available space, and budget. By understanding these factors and comparing different system types, you can choose an RO system that meets your needs while providing clean, safe, and great-tasting water.
Innovations in Reverse Osmosis Technology: Advancing Water Purification
High-Efficiency Membranes: Boosting Performance and Reducing Energy Use
Recent advancements in reverse osmosis technology have led to the development of high-efficiency membranes that significantly improve the performance of RO systems. Traditional membranes, while effective, often require high pressure to push water through their semi-permeable layers, leading to increased energy consumption. High-efficiency membranes address this issue by offering enhanced permeability, allowing water to pass through more easily while maintaining the same level of contaminant removal.
These advanced membranes are designed with improved materials and structures, such as thin-film composite layers and nanotechnology enhancements. They not only reduce energy requirements but also increase water recovery rates, making the purification process more efficient. For example, some modern membranes can achieve recovery rates of up to 60–80%, compared to the 40–50% typical of older systems. This improvement translates to lower operational costs and a reduced environmental footprint, making high-efficiency membranes a game-changer for both residential and industrial applications.
Smart RO Systems with IoT Integration: Enhancing User Experience
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology into reverse osmosis systems has revolutionized the way users interact with and maintain their water purification systems. Smart RO systems now come equipped with sensors, connectivity features, and mobile app integration, allowing users to monitor and control their systems remotely.
- Real-Time Monitoring: IoT-enabled RO systems provide real-time data on water quality, filter status, and system performance. Users can receive alerts when filters need replacement or when the system detects a drop in efficiency, ensuring timely maintenance.
- Remote Control: With mobile apps, users can adjust system settings, initiate cleaning cycles, or even shut down the system remotely. This level of control adds convenience and peace of mind, especially for busy households or businesses.
- Data Analytics: Smart systems collect and analyze usage data, helping users optimize water consumption and identify potential issues before they become major problems.
These innovations not only improve the user experience but also extend the lifespan of RO systems by ensuring they operate at peak efficiency. As IoT technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more advanced features, such as predictive maintenance and AI-driven optimization.
Sustainable Solutions to Reduce Wastewater: Addressing Environmental Concerns
One of the most significant challenges of reverse osmosis technology has been the generation of wastewater during the purification process. Traditional RO systems can waste two to three gallons of water for every gallon of purified water produced. However, recent innovations have focused on developing sustainable solutions to minimize this waste.
- Zero-Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Systems: ZLD technology captures and treats wastewater, recovering nearly all of the water for reuse. This approach is particularly beneficial for industrial applications, where water conservation is critical.
- Advanced Recovery Systems: Modern RO systems now feature advanced recovery technologies that increase water efficiency. For instance, some systems use energy recovery devices to recycle pressure energy, reducing both wastewater and energy consumption.
- Dual-Pass RO Systems: In dual-pass systems, the wastewater from the first pass is treated again to extract additional purified water. This method significantly reduces the overall waste generated by the system.
These sustainable innovations not only address environmental concerns but also make reverse osmosis more cost-effective in the long run. By reducing water waste and energy use, these advancements align with global efforts to promote sustainable water management practices.
The Future of Reverse Osmosis Technology
The continuous evolution of reverse osmosis technology, driven by high-efficiency membranes, IoT integration, and sustainable solutions, is transforming the water purification landscape. These innovations not only enhance system performance and user convenience but also address critical environmental challenges, paving the way for a more efficient and sustainable future in water treatment.
FAQs About Reverse Osmosis
Q: Is RO water safe to drink?
A: Yes, reverse osmosis water is completely safe to drink. RO systems remove harmful contaminants like lead, arsenic, nitrates, and bacteria, ensuring the water is clean and safe. While the process also removes some minerals, these are typically inorganic and not essential for health. A balanced diet provides the necessary minerals your body needs.
Q: How much water does an RO system waste?
A: Traditional reverse osmosis systems waste about 2–3 gallons of water for every gallon of purified water produced. However, modern systems with water-saving technologies have significantly reduced this ratio, with some achieving recovery rates of up to 80%. You can also reuse wastewater for non-potable purposes like irrigation or cleaning to minimize waste.
Q: Can RO remove fluoride and arsenic?
A: Yes, reverse osmosis effectively removes fluoride and arsenic from water. The semi-permeable membrane blocks these contaminants, reducing their levels to safe or undetectable amounts. This makes RO systems an excellent choice for areas with high concentrations of these harmful substances in the water supply.
Q: How often should I replace the filters in an RO system?
A: You should replace pre-filters (sediment and carbon filters) every 6–12 months, depending on water quality and usage. Post-filters typically need replacement every 12 months, while the RO membrane lasts 2–3 years. Regular maintenance ensures the system operates efficiently and delivers high-quality water.
Q: Does RO water taste different?
A: Yes, reverse osmosis water often tastes cleaner and fresher because it removes impurities like chlorine, dissolved salts, and other contaminants that can affect flavor. Many users find RO water more enjoyable to drink compared to untreated tap water.
Q: Can an RO system remove bacteria and viruses?
A: Reverse osmosis can remove most bacteria and some viruses due to the membrane’s tiny pore size. However, it may not eliminate all microorganisms. For added protection, many systems include UV sterilizers or additional filters to ensure complete microbial safety.
Conclusion
Reverse osmosis stands out as a highly effective water purification method, removing a wide range of contaminants to deliver clean, safe, and great-tasting water. By utilizing a semi-permeable membrane and advanced filtration stages, RO systems address diverse needs, from residential drinking water to industrial applications. Its ability to improve water quality, enhance taste, and support sustainable practices makes it an invaluable solution for households and businesses alike. If you’re looking for a reliable way to ensure safe water for your specific needs, exploring reverse osmosis systems could be the perfect step forward.
Related Posts
- Self-Cleaning Filters: Types, How They Work & Automatic Filtration
- Understanding the Key Differences Between Strainers and Filters
- Backwash Filters Simplified: Types, Benefits, and How to Maximize Filtration Efficiency
- Sintering Techniques: Metal Sintering and Furnace Types
- 304 Stainless Steel Wire Mesh Filter Cloth – Micron Filter Mesh
- Understanding Acrylic Fabric: Properties & Production
- Industrial Cartridge Filters: A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Filter for Your Needs
- Filtration vs. Reverse Osmosis: A Clear Guide to Choosing the Right Water Purification Method




