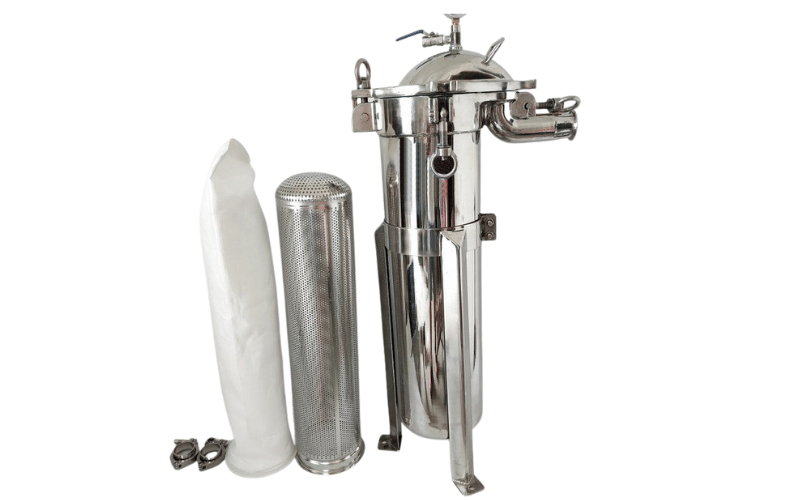
Filter housing systems are essential components in industrial and commercial filtration, designed to protect and support filter cartridges while ensuring efficient contaminant removal. These systems play a critical role in maintaining water quality, safeguarding equipment, and optimizing filtration processes. This article aims to explore their components, various types, and key benefits, while providing practical insights to help you make informed decisions.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are Filter Housing Systems?
Defining Filter Housing Systems and Their Role
Filter housing systems are specialized enclosures designed to securely hold filter elements, such as cartridges or bags, within a filtration setup. These systems serve as the structural backbone of filtration processes, ensuring that water, air, or other fluids pass through the filter media effectively while preventing leaks or bypasses. By providing a controlled environment for the filter elements, housing systems enhance the efficiency and reliability of contaminant removal, making them indispensable in both industrial and commercial applications.
The design of filter housings varies depending on the specific filtration requirements, but they typically include features like inlet and outlet ports, sealing mechanisms, and pressure-resistant materials. These components work together to maintain consistent flow rates, withstand operational pressures, and protect the filter media from external damage. Whether used in single-stage or multi-stage filtration systems, filter housings play a critical role in optimizing performance and extending the lifespan of the filter elements they contain.
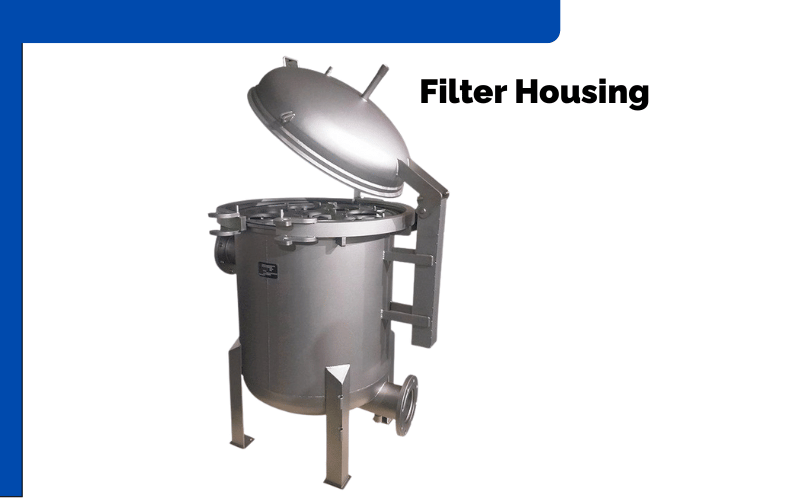

Applications Across Key Industries
Filter housing systems are widely used across a range of industries, each with unique filtration needs. In water treatment facilities, these systems are essential for purifying drinking water, removing sediments, and ensuring compliance with safety standards. Municipal water plants often rely on robust stainless steel housings to handle high volumes and pressures, ensuring consistent delivery of clean water to communities.
In the pharmaceutical sector, filter housings are critical for maintaining sterility and precision during the production of medications and vaccines. These systems are designed to accommodate high-performance filters that remove bacteria, endotoxins, and other microscopic contaminants. The use of durable, corrosion-resistant materials ensures that the housings can withstand rigorous cleaning and sterilization processes without compromising their integrity.
The food and beverage industry also depends heavily on filter housing systems to maintain product quality and safety. From filtering water used in brewing to removing impurities from oils and syrups, these systems ensure that contaminants do not affect the taste, appearance, or safety of the final product. For example, breweries often use multi-stage filtration setups with specialized housings to achieve the desired clarity and flavor in their beverages.
By adapting to the specific demands of these diverse industries, filter housing systems demonstrate their versatility and importance in modern filtration processes. Their ability to enhance efficiency, protect filter elements, and ensure consistent results makes them a cornerstone of industrial and commercial operations.
Key Components of Filter Housing Systems
Housing Body: The Foundation of Durability and Performance
The housing body forms the core structure of a filter housing system, providing the enclosure that holds the filter element securely in place. The material used for the housing body significantly impacts its durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. Stainless steel is a popular choice for industrial and commercial filtration systems due to its strength, longevity, and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures. It is particularly well-suited for demanding environments, such as water treatment plants and pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities, where durability and hygiene are crucial.
Polypropylene, on the other hand, is a lightweight and cost-effective alternative often used in residential or less demanding applications. This material offers excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for filtering corrosive fluids or chemicals. While it may not match the strength of stainless steel, polypropylene housings are highly effective for applications with lower pressure requirements. By selecting the appropriate housing material, users can ensure optimal performance and longevity for their filtration systems.
Inlet and Outlet Ports: Regulating Fluid Flow
Inlet and outlet ports are essential components of filter housing systems, as they control the flow of fluids entering and exiting the housing. These ports are strategically designed to ensure smooth and efficient fluid movement, minimizing turbulence and pressure drops that could affect filtration performance. The size and configuration of the ports vary depending on the system’s capacity and application, with larger ports typically used for high-flow systems.
Proper alignment of the inlet and outlet ports is crucial for maintaining consistent flow rates and preventing leaks. Some advanced filter housings feature multi-port designs, allowing for greater flexibility in installation and operation. For example, systems with multiple inlets can accommodate different fluid sources, while adjustable outlets enable precise control over the direction and rate of flow. By optimizing the design and placement of these ports, filter housing systems can achieve superior efficiency and reliability.
Sealing and Closure Mechanisms: Preventing Bypass and Ensuring Integrity
Sealing and closure mechanisms play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of a filter housing system. These components ensure that unfiltered fluid does not bypass the filter element, which could compromise the quality of the output. High-quality seals, such as O-rings or gaskets, create a tight barrier between the housing body and the filter element, preventing leaks and ensuring that all fluid passes through the filter media.
Closure mechanisms, such as clamps, bolts, or threaded caps, secure the housing body and maintain a tight seal during operation. These mechanisms must be robust enough to withstand the pressure and temperature fluctuations that occur during filtration. For instance, industrial systems often utilize heavy-duty clamps or swing bolts to ensure a secure and reliable closure. In contrast, residential systems may rely on simpler threaded caps for ease of use. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components are essential to prevent wear and ensure consistent performance.
Additional Features: Enhancing Functionality and Safety
Modern filter housing systems often include additional features that enhance their functionality and safety. Pressure relief valves are a common addition, designed to release excess pressure within the housing and prevent damage to the system. These valves are critical in high-pressure applications, where sudden spikes could compromise the housing or filter element.
Drain valves are another helpful feature, allowing users to easily remove accumulated fluid or contaminants from the housing. This simplifies maintenance and helps extend the lifespan of the filter element. Mounting brackets are also frequently included, providing a secure and stable installation for the housing system. These brackets ensure that the housing remains in place during operation, reducing the risk of leaks or misalignment.
By incorporating these additional features, filter housing systems offer greater convenience, safety, and efficiency, making them a reliable choice for a wide range of filtration needs.
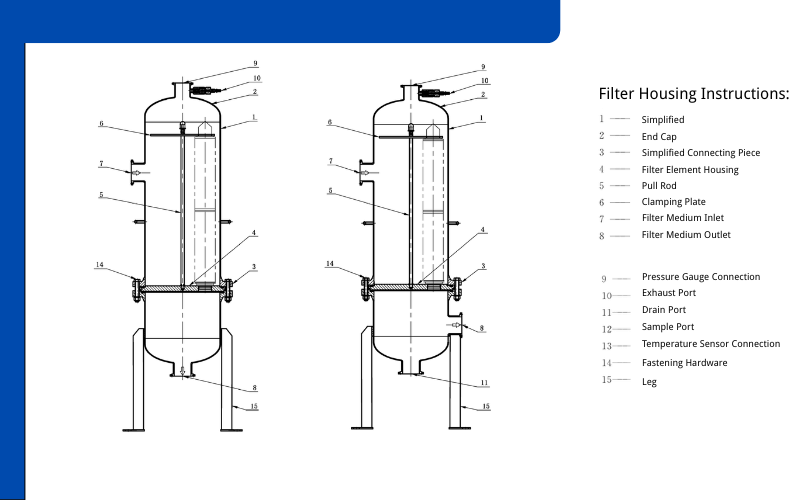
Types of Filter Housing Systems
Single Cartridge Housing: Compact and Cost-Effective Solutions
Single cartridge housings are designed to hold one filter cartridge, making them a compact and economical choice for small-scale applications. These systems are commonly used in residential settings, laboratories, and small industrial processes where the filtration demand is relatively low. Their straightforward design allows for easy installation and maintenance, making them a practical option for users seeking simplicity and efficiency.
Despite their smaller size, single cartridge housings can accommodate a variety of filter types, including sediment, carbon, and pleated filters, depending on the specific filtration needs. They are ideal for applications such as point-of-use water filtration, where space constraints and cost considerations are key factors. By selecting the appropriate cartridge, users can achieve effective contaminant removal without the need for a larger, more complex system.
Multi-Cartridge Housing: High Flow Rates and Multi-Stage Filtration
Multi-cartridge housings are engineered to hold multiple filter cartridges within a single housing unit, making them suitable for applications requiring high flow rates or multi-stage filtration. These systems are commonly found in industrial and commercial settings, such as water treatment plants, chemical processing facilities, and large-scale food production. By distributing the filtration workload across multiple cartridges, these housings enhance efficiency and extend the lifespan of each filter.
The modular design of multi-cartridge housings allows for customization based on specific filtration requirements. For example, users can combine different types of cartridges, such as sediment and activated carbon filters, to achieve comprehensive contaminant removal. Additionally, these systems are designed to handle higher pressures and larger volumes, ensuring consistent performance even in demanding environments. Their scalability and versatility make them a preferred choice for industries with complex filtration needs.

Bag Filter Housing: Efficient for Larger Particles
Bag filter housings are specifically designed to filter larger particles and debris, making them ideal for industrial processes such as wastewater treatment, oil filtration, and paint production. These systems use filter bags instead of cartridges, which are capable of capturing high volumes of contaminants without frequent replacements. The bags are easy to remove and replace, simplifying maintenance and reducing downtime.
Bag filter housings are particularly effective in applications where the primary goal is to remove coarse particles or protect downstream equipment from damage. Their robust construction and ability to handle high flow rates make them a reliable choice for heavy-duty filtration tasks. Additionally, the availability of different bag materials and micron ratings allows users to tailor the system to their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
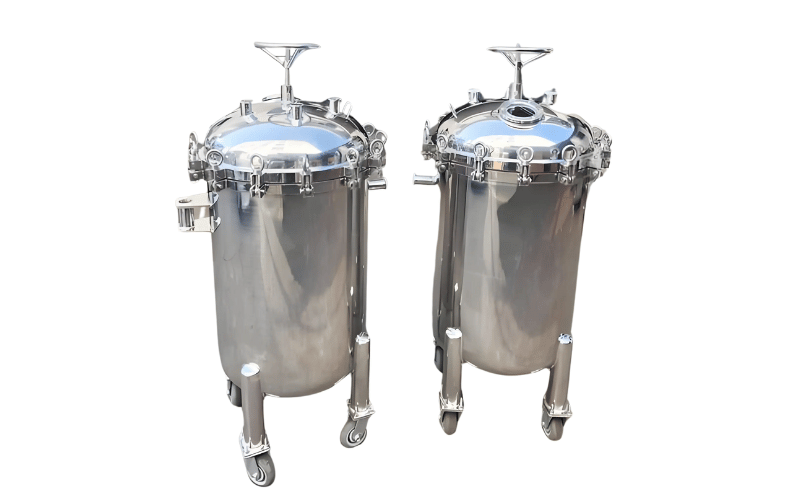

Stainless Steel Housing: Durability for Harsh Environments
Stainless steel housings are renowned for their durability, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. These features make them an excellent choice for harsh environments, such as chemical processing plants, marine applications, and high-temperature industrial processes. Stainless steel housings are also widely used in water treatment facilities and pharmaceutical manufacturing, where hygiene and reliability are critical.
The robust construction of stainless steel housings ensures long-term performance and minimal maintenance, even under challenging conditions. They are compatible with a wide range of filter types and can be customized to meet specific operational requirements. While they may have a higher upfront cost compared to other materials, their longevity and resilience make them a cost-effective investment for demanding applications.
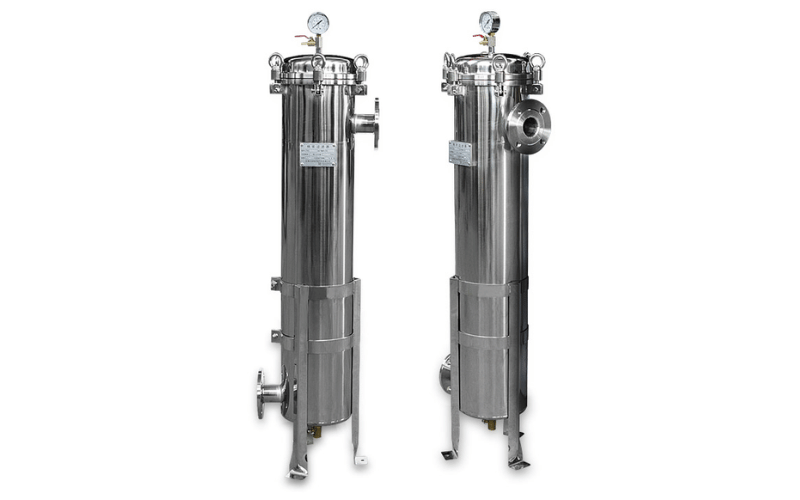

Plastic Housing: Lightweight and Economical for Residential Use
Plastic housings, typically made from materials like polypropylene or PVC, are lightweight, affordable, and easy to install, making them a popular choice for residential and light commercial applications. These housings are commonly used in point-of-entry and point-of-use water filtration systems, where the filtration demands are moderate, and cost considerations are important.
Despite their lower cost, plastic housings offer excellent chemical resistance, making them suitable for filtering water with high chlorine content or other corrosive substances. They are available in various sizes and configurations, allowing users to select a system that meets their specific needs. While not as durable as stainless steel, plastic housings provide a practical and economical solution for everyday filtration tasks.
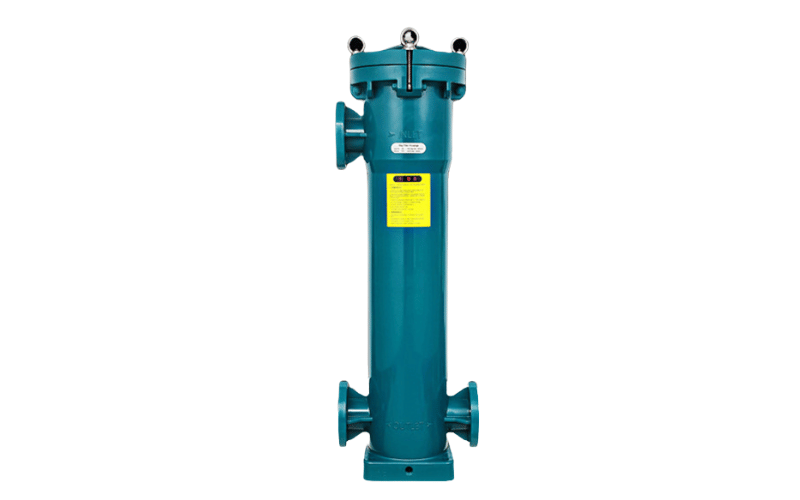

Sanitary Housing: Hygiene-Critical Solutions for Food and Pharmaceuticals
Sanitary housings are specifically designed for industries where hygiene and cleanliness are paramount, such as food and beverage production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and biotechnology. These housings are constructed from high-grade stainless steel and feature smooth, polished surfaces that prevent the buildup of contaminants and facilitate easy cleaning.
In addition to their hygienic design, sanitary housings often include features like tri-clamp connections and crevice-free construction to eliminate potential contamination points. They are compatible with sterilization processes, such as steam cleaning, ensuring compliance with strict industry standards. By providing a sterile and reliable filtration environment, sanitary housings help maintain product quality and safety in applications that require strict hygiene standards.

Benefits of Using Filter Housing Systems
Enhanced Filtration Efficiency: Ensuring Thorough Contaminant Removal
Filter housing systems are designed to optimize the filtration process, ensuring that contaminants are effectively removed from water, air, or other fluids. By securely holding filter elements in place and preventing bypass, these systems ensure that all fluid passes through the filter media. This controlled environment enhances the efficiency of contaminant removal, whether it involves sediments, bacteria, or chemical impurities.
Advanced designs, such as multi-cartridge or multi-stage housings, further improve filtration by allowing the use of different filter types in a single system. For example, a combination of sediment and activated carbon filters can remove both particulate matter and chlorine, delivering cleaner and safer output. The ability to maintain consistent flow rates and pressure also contributes to the thoroughness of the filtration process, making these systems indispensable for industries that demand high-quality results.
Durability and Longevity: The Value of High-Quality Materials
The durability of filter housing systems is a key factor in their long-term performance and cost-effectiveness. High-quality materials, such as stainless steel and reinforced plastics, ensure that the housings can withstand the pressures, temperatures, and chemical exposures common in industrial and commercial applications. Stainless steel housings, for instance, are highly resistant to corrosion and wear, making them ideal for harsh environments like chemical processing plants or marine applications.
Reinforced plastic housings, while more lightweight and economical, also offer excellent resistance to chemicals and are suitable for residential or light commercial use. By investing in durable materials, users can reduce the frequency of replacements and minimize maintenance costs, ensuring that their filtration systems remain reliable over time. The longevity of these housings not only saves money but also reduces environmental waste, aligning with sustainability goals.
Customizability: Tailored Solutions for Diverse Applications
One of the standout benefits of filter housing systems is their customizability, which allows them to meet the specific needs of various industries and applications. These systems are available in a wide range of sizes, materials, and configurations, enabling users to select the most suitable option for their requirements. For example, single cartridge housings are perfect for small-scale applications, while multi-cartridge systems are better suited for high-flow industrial processes.
Additionally, users can choose from different sealing mechanisms, port sizes, and mounting options to ensure compatibility with their existing setups. Some housings are designed to accommodate specialized filters, such as sanitary housings for food and pharmaceutical industries or bag housings for heavy-duty filtration tasks. This flexibility makes filter housing systems a versatile solution that can be adapted to a wide range of operational demands.
Ease of Maintenance: Simplifying Upkeep and Reducing Downtime
Filter housing systems are designed with user convenience in mind, incorporating features that simplify maintenance and reduce downtime. Many housings include drain valves, which allow users to easily remove accumulated fluid or contaminants without disassembling the system. This feature is particularly useful in industrial settings, where quick and efficient maintenance is essential to avoid production delays.
In addition to drain valves, most housings are designed for easy filter replacement, with accessible closures and straightforward mechanisms. For example, threaded caps or swing bolts enable users to open the housing quickly, replace the filter element, and reseal the system without specialized tools. Regular maintenance becomes less of a burden, ensuring that the filtration system operates at peak efficiency with minimal effort. By streamlining upkeep, these features contribute to the overall reliability and cost-effectiveness of filter housing systems.
Choosing the Right Filter Housing System
Assess the Type of Fluid and Contaminants
Selecting the right filter housing system begins with understanding the type of fluid being filtered and the contaminants that need to be removed. Different fluids, such as water, oil, or chemicals, have unique properties that influence the choice of housing and filter media. For instance, water filtration may require housings compatible with sediment or carbon filters, while chemical filtration demands materials resistant to corrosive substances. Identifying the specific contaminants—whether they are sediments, bacteria, or dissolved chemicals—helps determine the appropriate filter type and micron rating for effective removal.
Additionally, consider whether the filtration process involves single-stage or multi-stage systems. Multi-stage setups may require housings that can accommodate various filter types, such as sediment filters for larger particles followed by activated carbon filters for finer impurities. By thoroughly assessing the fluid and its contaminants, you can ensure that the housing system meets your filtration needs effectively.
Consider Operating Conditions Like Pressure and Temperature
Operating conditions, such as pressure and temperature, play a critical role in determining the suitability of a filter housing system. High-pressure applications, such as industrial water treatment or oil filtration, require housings made from robust materials like stainless steel to withstand the stress. Conversely, low-pressure systems, such as residential water filtration, can often use plastic housings, which are more lightweight and cost-effective.
Temperature is another important factor to evaluate. For processes involving high temperatures, such as steam filtration or hot water systems, stainless steel housings are ideal due to their heat resistance. On the other hand, plastic housings may deform or degrade under extreme heat, making them unsuitable for such applications. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for pressure and temperature ratings to ensure the housing system can handle your operational requirements without compromising performance or safety.
Match the Housing Material to the Application
The material of the filter housing significantly impacts its durability, compatibility, and overall performance. Stainless steel housings are a top choice for demanding industrial applications due to their strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to handle high pressures and temperatures. They are particularly well-suited for environments where exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme conditions is common, such as chemical processing plants or marine operations.
For less demanding applications, such as residential water filtration or light commercial use, plastic housings made from materials like polypropylene or PVC offer a more economical and lightweight alternative. These housings provide excellent chemical resistance and are easy to install, making them a practical choice for everyday filtration needs. Matching the housing material to the specific application ensures optimal performance, longevity, and cost-efficiency.
Evaluate Flow Rate and Filtration Capacity
Flow rate and filtration capacity are critical factors to consider when choosing a filter housing system. The flow rate determines how quickly the fluid can pass through the system, while the filtration capacity indicates the volume of fluid the system can handle before requiring maintenance or replacement. For high-flow applications, such as municipal water treatment or large-scale industrial processes, multi-cartridge housings or bag filter systems are ideal, as they can accommodate larger volumes and maintain consistent performance.
In contrast, single cartridge housings are better suited for low-flow applications, such as point-of-use water filtration in homes or small businesses. When evaluating flow rate, ensure that the housing system can maintain adequate pressure and efficiency without causing bottlenecks or pressure drops. Additionally, consider the frequency of filter replacements and the ease of maintenance to ensure the system remains cost-effective and reliable over time. By carefully assessing flow rate and capacity, you can select a housing system that meets your operational demands while delivering consistent results.
Innovations in Filter Housing Technology
Smart Monitoring Systems: Real-Time Performance Tracking with IoT
The integration of IoT technology into filter housing systems has revolutionized how filtration processes are monitored and managed. Smart monitoring systems equipped with sensors can track critical performance metrics, such as flow rate, pressure, and contaminant levels, in real time. These systems provide users with instant updates via mobile apps or connected devices, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of system failures.
For example, IoT-enabled housings can send alerts when a filter is nearing its capacity or when pressure drops indicate clogging. This eliminates the guesswork involved in filter replacement schedules, ensuring that the system operates at peak efficiency. Some advanced systems even offer predictive analytics, using historical data to forecast maintenance needs and optimize performance. By adopting smart monitoring technology, industries can reduce downtime, improve operational efficiency, and extend the lifespan of their filtration systems.
Eco-Friendly Designs: Sustainable Materials and Reusable Components
As sustainability becomes a priority across industries, filter housing technology has evolved to include eco-friendly designs that minimize environmental impact. Manufacturers are increasingly using sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics or biodegradable polymers, to produce housings that are both durable and environmentally responsible. These materials reduce the carbon footprint of production and disposal, aligning with global efforts to promote sustainability.
Reusable components are another key innovation in eco-friendly filter housing systems. For instance, some housings are designed to accommodate washable and reusable filter elements, significantly reducing waste compared to disposable filters. Additionally, modular designs allow users to replace individual parts, such as seals or valves, without discarding the entire housing. These advancements not only lower operational costs but also contribute to a more sustainable approach to filtration, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious businesses.
Advanced Sealing Mechanisms: Enhancing Efficiency and Preventing Leaks
Innovations in sealing mechanisms have greatly improved the efficiency and reliability of filter housing systems. Traditional seals, such as O-rings and gaskets, have been upgraded with advanced materials and designs that provide a tighter, more durable seal. These improvements prevent leaks and ensure that all fluid passes through the filter media, maximizing contaminant removal and system performance.
Some modern housings feature dynamic sealing systems that adapt to changes in pressure or temperature, maintaining a secure seal under varying operating conditions. For example, spring-loaded seals can adjust to fluctuations in pressure, ensuring consistent performance even in high-stress environments. Additionally, innovations like double-seal designs or integrated locking mechanisms provide an extra layer of protection against leaks, making these systems more reliable for critical applications. By enhancing sealing technology, manufacturers have created filter housings that deliver superior efficiency and long-term durability.
Applications of Filter Housing Systems
Water Treatment: Removing Sediments and Impurities
Filter housing systems play a critical role in water treatment processes, ensuring the delivery of clean and safe water for residential, commercial, and industrial use. These systems are designed to remove sediments, debris, and other impurities from raw water sources, such as rivers, lakes, or groundwater. By securely holding filter elements, such as sediment cartridges or activated carbon filters, the housings ensure that contaminants are effectively captured, leaving the water clear and safe for consumption or further processing.
Municipal water treatment plants often rely on multi-cartridge housings to handle high flow rates and large volumes of water. These systems are also equipped with durable materials, such as stainless steel, to withstand the pressures and demands of continuous operation. In addition to municipal applications, filter housings are widely used in private water systems, such as well water filtration, to remove particulates and improve water quality. Their versatility and efficiency make them indispensable in maintaining water safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring Sterility in Drug Manufacturing
In the pharmaceutical industry, maintaining sterility and precision is crucial, and filter housing systems play a vital role in achieving these goals. These systems are used in various stages of drug manufacturing, including water purification, air filtration, and the production of injectable medications. By holding high-performance filters, such as membrane or pleated cartridges, the housings ensure the removal of bacteria, endotoxins, and other microscopic contaminants that could compromise product safety.
Sanitary filter housings, constructed from polished stainless steel, are specifically designed for applications that require high hygiene standards. They feature smooth, crevice-free surfaces that prevent the buildup of contaminants and facilitate easy cleaning. These housings are also compatible with sterilization processes, such as steam cleaning, ensuring compliance with stringent industry standards. By providing a sterile and reliable filtration environment, filter housing systems help pharmaceutical manufacturers maintain product integrity and meet regulatory requirements.
Oil and Gas: Filtering Contaminants in Drilling Fluids
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on filter housing systems to ensure the efficiency and safety of its operations. These systems are used to filter contaminants from drilling fluids, hydraulic oils, and other process liquids, preventing equipment damage and maintaining operational efficiency. For example, bag filter housings are commonly employed to remove large particles and debris from drilling fluids, protecting pumps and other critical equipment from wear and tear.
In addition to drilling operations, filter housings are used in the refining process to remove impurities from crude oil and ensure the quality of the final product. The housings are often constructed from heavy-duty materials, such as stainless steel, to withstand the harsh conditions and high pressures typical of oil and gas applications. By providing reliable filtration, these systems help reduce downtime, extend equipment lifespan, and improve overall process efficiency.
Food and Beverage: Maintaining Product Safety and Quality
In the food and beverage industry, filter housing systems are essential for maintaining product safety, consistency, and quality. These systems are used to filter water, oils, syrups, and other ingredients, ensuring that contaminants do not compromise the taste, appearance, or safety of the final product. For example, breweries use filter housings to remove sediments and impurities from water and beer, achieving the desired clarity and flavor profile.
Sanitary housings are particularly important in this industry, as they are designed to meet strict hygiene standards. Constructed from polished stainless steel, these housings prevent contamination and are easy to clean, making them ideal for applications such as dairy production, juice processing, and bottled water filtration. By ensuring the removal of unwanted particles and microorganisms, filter housing systems help food and beverage manufacturers deliver high-quality products that meet consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Filter housing systems play a vital role in achieving efficient and reliable filtration across various industries, ensuring clean water, safe products, and optimized processes. Selecting the right system tailored to your specific needs is essential for maximizing performance and longevity. Consult experts to explore customized solutions that align with your operational goals.





