Stainless steel filter housings are essential components in industrial filtration systems, offering unmatched durability and performance. These housings securely hold filter cartridges or bags, ensuring efficient removal of contaminants from liquids or gases. Their ability to withstand high pressures, extreme temperatures, and corrosive environments makes them indispensable in industries like water treatment, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals.
Water treatment facilities use stainless steel housings to filter sediment and bacteria, ensuring clean water. In the food and beverage sector, they maintain product quality while meeting strict hygiene standards. Pharmaceutical manufacturers rely on them for ultrapure water and sterile filtration critical to production.
Known for its corrosion resistance and reliability, stainless steel outperforms other materials in demanding conditions. This guide will help you explore the benefits, applications, and selection criteria for choosing the right stainless steel filter housing for your needs.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Material Advantage: Why Stainless Steel Stands Out
When it comes to industrial filtration, the material of your filter housing can make or break your system’s performance. Stainless steel has earned its place as the gold standard, offering a combination of strength, reliability, and versatility that other materials simply can’t match. Let’s explore the key reasons why stainless steel stands out and how it delivers unmatched value in demanding industrial environments.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Stainless steel’s ability to resist rust and chemical damage is one of its most celebrated qualities. This resistance comes from its chromium content, which forms a thin, self-repairing chromium oxide layer on the surface. This layer acts as a shield, protecting the material from moisture, oxygen, and corrosive chemicals.
For example, in water treatment plants, where exposure to chlorides and other corrosive agents is common, stainless steel housings maintain their integrity far longer than plastic or carbon steel alternatives. However, not all stainless steel is created equal.
- 304 Stainless Steel: This grade works well in environments with low to moderate exposure to corrosive elements. It’s a cost-effective choice for applications like general water filtration or food processing where the risk of chemical exposure is minimal.
- 316 Stainless Steel: For harsher environments, such as those involving saltwater, acids, or aggressive chemicals, 316 stainless steel is the better option. Its higher molybdenum content enhances its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making it ideal for marine applications or chemical processing plants.
Choosing the right grade ensures your filter housing can withstand the specific challenges of your environment, reducing the risk of failure and extending its lifespan.
Thermal and Pressure Tolerance
Industrial processes often involve extreme conditions, and stainless steel excels in handling both high temperatures and pressures. Unlike plastic or other materials that can warp, crack, or degrade under stress, stainless steel maintains its structural integrity, ensuring reliable performance.
- High-Temperature Applications: Stainless steel can withstand temperatures well above 500°F (260°C), making it suitable for steam filtration or processes involving hot liquids. For example, in a pharmaceutical facility, stainless steel housings can handle the high heat required for sterilization without compromising performance.
- High-Pressure Environments: In industries like oil and gas, where systems operate under intense pressure, stainless steel housings provide the strength needed to prevent leaks or ruptures. Their robust construction ensures safety, especially when dealing with volatile or high-temperature liquids.
By choosing stainless steel, you gain peace of mind knowing your system can handle the toughest conditions without compromising safety or efficiency.
Hygienic Properties
Hygiene is non-negotiable in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology. Stainless steel’s non-porous surface resists bacterial growth and contamination, making it the material of choice for applications where cleanliness is critical.
- Bacterial Resistance: Unlike porous materials that can harbor bacteria, stainless steel’s smooth surface prevents microorganisms from embedding themselves. This property is especially important in processes like dairy production or pharmaceutical manufacturing, where even minor contamination can have serious consequences.
- Ease of Cleaning: Stainless steel is compatible with Clean-In-Place (CIP) systems, which allow for automated cleaning and sterilization without disassembling the equipment. This feature saves time, reduces labor costs, and ensures consistent hygiene standards. For example, a brewery can use CIP systems to clean stainless steel filter housings between batches, maintaining product quality without interrupting production.
Stainless steel’s hygienic properties not only protect your products but also help you meet stringent regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance and customer trust.
Stainless steel filter housings offer a material advantage that’s hard to beat. Their corrosion resistance, durability, thermal and pressure tolerance, and hygienic properties make them a reliable choice for even the most demanding industrial applications. By understanding these benefits, you can confidently select stainless steel as the foundation of a robust and efficient filtration system.
Benefits of Stainless Steel Filter Housings
Stainless steel filter housings bring more than just strength to the table—they deliver a range of benefits that make them a smart investment for industrial filtration systems. From durability to environmental advantages, these housings address critical operational needs while offering long-term value. Let’s explore their key benefits in detail.
Long-Term Durability: Withstanding Harsh Environments
Stainless steel filter housings are built to last, even in the most challenging conditions. Their resistance to corrosion, high pressures, and extreme temperatures ensures they perform reliably over time, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
For example, in chemical processing plants, where exposure to corrosive substances like acids and alkalis is common, stainless steel housings maintain their structural integrity far longer than plastic or carbon steel alternatives. Similarly, in outdoor applications like water treatment facilities, stainless steel resists rust and weathering, ensuring consistent performance year after year.
By choosing stainless steel, you minimize downtime, lower maintenance costs, and avoid the hassle of frequent replacements, making it a cost-effective solution for long-term use.
Versatility Across Industries: Meeting Diverse Filtration Needs
One of stainless steel’s greatest strengths is its adaptability. These housings can handle a wide range of filtration applications, from coarse sediment removal to fine filtration of microorganisms and dissolved solids.
- Food and Beverage: Stainless steel housings meet strict hygiene standards, making them ideal for filtering water, syrups, or other liquids in beverage production.
- Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, these housings support sterile filtration processes, ensuring ultrapure water and contamination-free outputs.
- Oil and Gas: For high-pressure environments, stainless steel housings provide the strength needed to filter hydrocarbons or protect sensitive equipment.
This versatility allows stainless steel filter housings to seamlessly integrate into various industries, addressing unique challenges with precision and reliability.
Optimal Filtration Performance: Ensuring Clean Outputs
Stainless steel filter housings don’t just hold filters—they enhance their performance. Their robust construction ensures a tight seal, preventing bypassing and ensuring that all water or liquid passes through the filter media.
For instance, in a dairy processing plant, a stainless steel housing ensures that milk flows through the filter without contamination, maintaining product quality. In industrial water treatment, these housings prevent leaks or bypassing that could compromise water purity.
By maintaining a secure and efficient filtration process, stainless steel housings help deliver clean, reliable outputs with minimal risk of contamination.
Environmental Benefits: A Sustainable Choice
Stainless steel filter housings offer significant environmental advantages, making them a sustainable choice for industries looking to reduce their environmental footprint.
- Recyclability: Stainless steel is 100% recyclable, meaning old housings can be repurposed into new products rather than ending up in landfills.
- Longevity: Their long lifespan reduces waste generated from frequent replacements, unlike plastic housings that degrade quickly and require constant disposal.
- Lower Resource Use: Over time, the durability and reusability of stainless steel housings reduce the need for raw materials and energy used in manufacturing replacements.
For industries prioritizing sustainability, stainless steel filter housings align with environmental goals while delivering top-tier performance.
Stainless steel filter housings combine durability, versatility, performance, and sustainability into one powerful package. By investing in these housings, you not only enhance your filtration system’s reliability but also contribute to a more efficient and environmentally responsible operation.
Types of Stainless Steel Filter Housings
Stainless steel filter housings come in various designs, each tailored to meet specific operational needs. Whether you’re managing a small-scale process or a high-capacity industrial system, understanding the different types of housings ensures you select the right one for your application. Let’s break down the key types and their unique advantages.
Single Cartridge Housings: Compact and Ideal for Small-Scale Applications
Single cartridge housings are the workhorses of smaller systems, offering a compact and efficient solution for low-flow applications. These housings hold a single filter cartridge, making them easy to install and maintain.
For example, a laboratory might use a single cartridge housing to filter ultrapure water for experiments. At the same time, a small food processing facility could rely on it to remove sediment from water used in production. These housings are available in various sizes and materials, allowing you to match the cartridge to your specific filtration needs, whether it’s sediment removal or fine filtration.
Multi-Cartridge Housings: High Flow Rates for Industrial Use
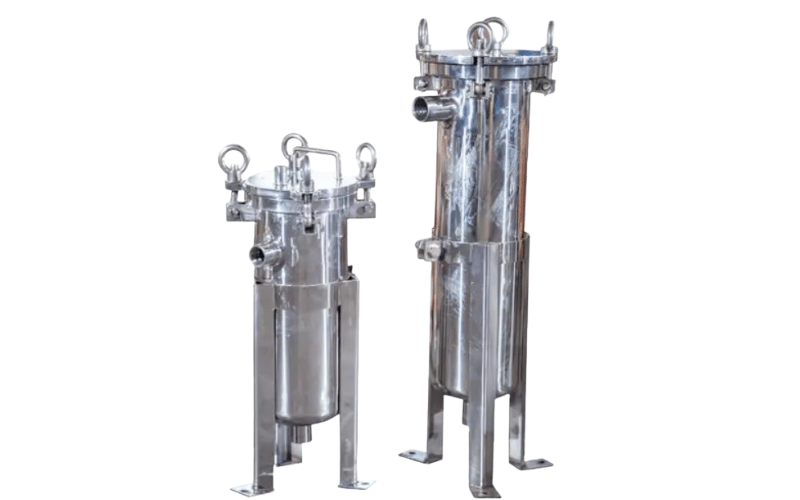
When dealing with high flow rates or large volumes of liquid, multi-cartridge housings step up to the challenge. These housings accommodate multiple filter cartridges, increasing filtration capacity and efficiency.
Industries like oil and gas or chemical processing often use multi-cartridge housings to handle demanding applications. For instance, a refinery might use a 10-cartridge housing to filter hydrocarbons at a rate of several hundred gallons per minute. These housings also allow for flexibility, as you can mix and match cartridges with different micron ratings to achieve multi-stage filtration in a single unit.

Bag Filter Housings: Effective for Removing Larger Particles
Bag filter housings are designed for applications where removing larger particles is the primary goal. These housings use filter bags, which are easy to replace and can handle high dirt loads without frequent maintenance.
For example, a wastewater treatment plant might use bag filter housings to remove debris and suspended solids before further treatment. Similarly, in the paint and coatings industry, these housings effectively capture clumps or impurities, ensuring a smooth final product. Their robust design and high dirt-holding capacity make them a cost-effective choice for pre-filtration or coarse filtration needs.

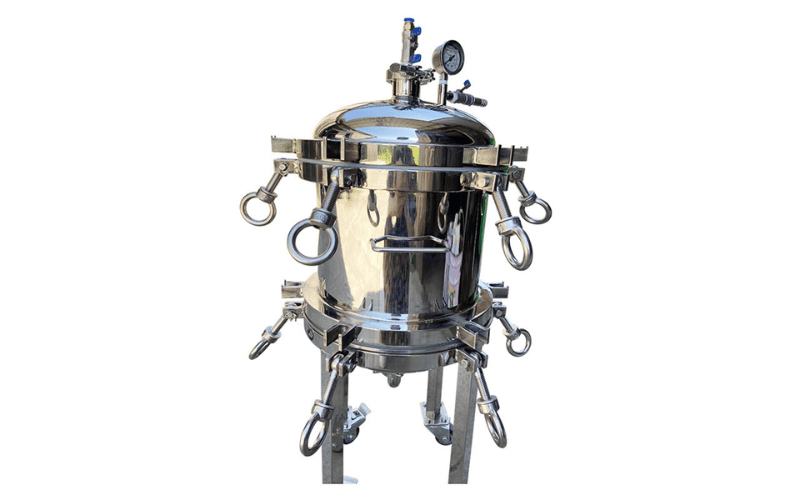
Sanitary Filter Housings: Designed for Food, Beverage, and Pharmaceutical Industries
Sanitary filter housings are purpose-built for industries where hygiene is critical. These housings feature polished surfaces, crevice-free designs, and compatibility with Clean-In-Place (CIP) systems to ensure the highest levels of cleanliness.
In a brewery, for instance, sanitary housings filter water and beer to remove impurities without compromising taste or quality. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, they ensure sterile filtration of liquids used in drug production. These housings often meet strict regulatory standards, such as FDA or 3-A certifications, making them a trusted choice for sensitive applications.

Custom Filter Housings: Tailored Solutions for Unique Requirements
Sometimes, standard housings don’t fit the bill. Custom filter housings offer tailored solutions for unique or complex filtration challenges. These housings can be designed to accommodate specific flow rates, pressure requirements, or space constraints.
For example, a power plant might require a custom housing to handle high-temperature steam filtration, while a chemical plant could need a specialized design to resist aggressive solvents. Working with a manufacturer to create a custom housing ensures the system meets your exact specifications, delivering optimal performance and reliability.
Understanding the types of stainless steel filter housings allows you to align your choice with your operational needs. Whether you need a compact single cartridge housing or a high-capacity multi-cartridge system, selecting the right type ensures efficient filtration and long-term success.
How to Choose the Right Stainless Steel Filter Housing
Selecting the right stainless steel filter housing requires a methodical approach. Each decision impacts the system’s performance, longevity, and ability to meet your operational goals. By breaking the process into clear steps, you can ensure your choice aligns with your specific needs and challenges. Let’s walk through the key considerations.
Step 1: Understand Your Filtration Needs
The first step in choosing the right filter housing is to define your filtration requirements. Without a clear understanding of what you need to filter and the conditions under which the system will operate, you risk selecting a housing that underperforms or fails prematurely.
- Type of Contaminants: Identify the impurities you need to remove. Are you dealing with suspended solids, dissolved chemicals, or microorganisms? For example, a water treatment plant might prioritize sediment removal, while a pharmaceutical facility focuses on sterile filtration to eliminate bacteria and viruses.
- Flow Rate, Pressure, and Temperature: Determine the operational parameters of your system. For instance, if your process requires filtering 100 gallons per minute at 150 psi and 200°F, you’ll need a housing that can handle those conditions without compromising performance.
By clearly defining these needs, you create a foundation for selecting a housing that meets both your technical and operational requirements.
Step 2: Match the Material to Your Application
The type of stainless steel you choose plays a critical role in the housing’s durability and resistance to environmental factors. Selecting the wrong material can lead to corrosion, leaks, or system failure.
- 304 Stainless Steel: This grade is suitable for general-purpose applications with low to moderate exposure to corrosive elements. For example, it works well in food and beverage filtration where the liquid is non-aggressive.
- 316 Stainless Steel: For harsher environments, such as those involving saltwater, acids, or aggressive chemicals, 316 stainless steel is the better choice. Its higher molybdenum content provides superior resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making it ideal for marine or chemical processing applications.
- Specialized Alloys: In extreme cases, such as high-temperature steam filtration or exposure to highly corrosive chemicals, consider specialized alloys like duplex stainless steel or Hastelloy. These materials offer enhanced strength and corrosion resistance for the most demanding conditions.
Matching the material to your application ensures the housing can withstand its environment and deliver reliable performance over time.
Step 3: Evaluate Operational Factors
Operational considerations often determine whether a filter housing integrates seamlessly into your system or becomes a source of frustration. Take the time to evaluate these factors before making your choice.
- Space Constraints: Measure the available space for the housing. Compact single cartridge housings work well in tight spaces, while multi-cartridge housings may require more room.
- Maintenance Needs: Consider how often the housing will need cleaning or cartridge replacement. For example, a self-cleaning housing might reduce labor costs in high-maintenance environments.
- Industry Standards: Ensure the housing meets relevant certifications, such as FDA compliance for food and beverage applications or ASME standards for pressure vessels. These certifications guarantee the housing is safe and suitable for your industry.
By addressing these factors, you can select a housing that fits seamlessly into your operations and minimizes downtime.
Step 4: Consider Seal and Gasket Compatibility
The seals and gaskets in your filter housing may seem like minor components, but they play a critical role in preventing leaks and maintaining system integrity. Choosing the wrong material can lead to compatibility issues, especially when dealing with aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures.
- O-Ring Materials: Match the gasket material to your application. For example:
- Silicone: Ideal for high-temperature applications but not suitable for aggressive chemicals.
- EPDM: Resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids and alkalis, making it a versatile choice for many industries.
- Viton: Excellent for handling aggressive chemicals and high temperatures, commonly used in chemical processing.
- Proper Fit: Ensure the seals and gaskets are properly sized and installed to prevent bypassing or leaks. A poorly fitted O-ring can compromise the entire filtration process.
By selecting the right seals and gaskets, you protect your system from leaks and ensure consistent filtration performance.
Choosing the right stainless steel filter housing involves more than just picking a product off the shelf. By understanding your filtration needs, matching the material to your application, evaluating operational factors, and ensuring seal compatibility, you can make an informed decision that delivers long-term reliability and efficiency.
Applications of Stainless Steel Filter Housings
Stainless steel filter housings are the unsung heroes of countless industries, quietly ensuring processes run smoothly, products meet quality standards, and systems remain efficient. Their versatility and durability make them indispensable across a wide range of applications. Let’s explore how these housings excel in specific industries and processes.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology
In pharmaceutical and biotech applications, precision and sterility are non-negotiable. Stainless steel filter housings rise to the challenge, providing the reliability and hygiene required for critical processes.
- Sterile Air Filtration: In cleanrooms and production facilities, stainless steel housings support sterile air filtration systems, ensuring that airborne contaminants don’t compromise sensitive operations. For example, they help maintain aseptic conditions during the production of injectable drugs.
- Solvent Filtration: Many pharmaceutical processes involve solvents that can be aggressive or volatile. Stainless steel housings, particularly those made from 316 stainless steel, resist chemical attack while ensuring the purity of the filtered solvent.
- Final Product Polishing: Before packaging, pharmaceutical products often undergo a final filtration step to remove any remaining particulates or impurities. Stainless steel housings ensure this critical step is performed with precision, safeguarding product quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
Food and Beverage Processing
The food and beverage industry demands filtration systems that can handle rigorous cleaning protocols and maintain product integrity. Stainless steel filter housings meet these demands with ease.
- Steam Sterilization: Many food and beverage processes rely on steam for sterilization. Stainless steel housings can withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved, ensuring reliable filtration of steam used in sterilizing equipment or packaging materials.
- Aggressive Cleaning Agents: Cleaning-In-Place (CIP) systems often use caustic or acidic cleaning agents to maintain hygiene. Stainless steel’s resistance to these chemicals ensures the housings remain durable and contamination-free.
- Specific Applications:
- Beer Filtration: Stainless steel housings are used to filter out yeast and other particulates, ensuring clarity and consistency in the final product.
- Dairy Processing: In milk and cheese production, these housings support the removal of bacteria and other impurities while maintaining strict hygiene standards.
- Bottled Water: For bottled water production, stainless steel housings ensure the removal of sediment and microorganisms, delivering a clean and safe product to consumers.
Industrial and Chemical Processing
Industrial and chemical processes often involve extreme conditions that demand robust filtration solutions. Stainless steel filter housings are built to handle these challenges head-on.
- High-Pressure and High-Temperature Environments: In applications like oil refining or power generation, stainless steel housings withstand the intense pressures and temperatures that would compromise other materials. For example, they can filter steam at over 500°F or handle pressures exceeding 300 psi.
- Filtering Corrosive Liquids and Solvents: Chemical processing plants often deal with aggressive substances like acids, alkalis, or solvents. Stainless steel, particularly 316 or specialized alloys, resists corrosion and ensures the integrity of the filtration system.
These housings not only protect downstream equipment but also ensure the safety and efficiency of the overall process.
High-Purity Water Treatment
High-purity water is essential in industries like electronics manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and power generation. Stainless steel filter housings play a critical role in maintaining the stringent quality standards required for these applications.
- Non-Leaching Components: Unlike plastic housings, stainless steel doesn’t leach contaminants into the water, ensuring the purity of the final product. This is especially important in semiconductor manufacturing, where even trace impurities can cause defects.
- Maintaining Water Quality Standards: Stainless steel housings support multi-stage filtration systems, including reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration, to achieve ultrapure water. For example, in power plants, they help produce demineralized water for use in boilers, preventing scaling and corrosion.
Stainless steel filter housings prove their worth across a diverse range of applications, from ensuring sterility in pharmaceuticals to withstanding the harsh conditions of industrial processes. By understanding their role in these industries, you can appreciate their value as a cornerstone of reliable and efficient filtration systems.
Maintenance Tips for Stainless Steel Filter Housings
Stainless steel filter housings are built to last, but even the toughest materials need proper care to perform at their best. Regular maintenance not only extends the life of your housing but also ensures consistent filtration performance. Let’s dive into actionable tips to keep your stainless steel filter housings in peak condition.
Regular Cleaning to Prevent Buildup of Contaminants
Contaminant buildup inside the housing can compromise filtration efficiency and even damage the system over time. Regular cleaning is essential to prevent these issues.
- Flush the Housing: After removing the filter cartridge or bag, flush the housing with clean water or an appropriate cleaning solution. For example, in food and beverage applications, use a food-grade cleaning agent to remove residue without introducing harmful chemicals.
- Remove Stubborn Deposits: If you notice scaling or biofilm, use a non-abrasive brush and a compatible cleaning solution to scrub the interior. Avoid harsh chemicals that could damage the housing’s protective chromium oxide layer.
- Dry Thoroughly: After cleaning, ensure the housing is completely dry before reassembly to prevent moisture-related issues like bacterial growth or corrosion.
By keeping the housing clean, you maintain optimal flow rates and filtration efficiency while reducing the risk of contamination.
Inspect for Damage and Address Promptly
Even stainless steel isn’t invincible. Regular inspections help you catch and address potential issues before they escalate.
- Check for Dents and Scratches: Physical damage, such as dents or deep scratches, can weaken the housing and compromise its ability to withstand pressure. For example, a dented housing in a high-pressure system could lead to leaks or even failure.
- Look for Corrosion: While stainless steel resists corrosion, exposure to harsh chemicals or improper cleaning can cause localized corrosion. Inspect the housing for signs of pitting or discoloration, especially around welds or joints.
- Inspect Seals and Gaskets: Damaged or worn seals can lead to leaks or bypassing. Check for cracks, deformation, or hardening, and replace seals as needed.
Promptly addressing damage ensures the housing remains safe and reliable, even in demanding conditions.
Use Compatible Filters to Maintain Efficiency
The filter cartridge or bag you choose directly impacts the performance of your housing. Using incompatible filters can reduce efficiency or even damage the housing.
- Match the Filter to the Application: For example, if you’re filtering aggressive chemicals, choose a filter material that can withstand those conditions without degrading.
- Ensure Proper Fit: A poorly fitting filter can allow contaminants to bypass the media, defeating the purpose of filtration. Always use filters designed for your specific housing model.
- Monitor Filter Life: Replace filters according to the manufacturer’s guidelines or when you notice a drop in performance, such as reduced flow rates or increased pressure drops.
Using the right filters ensures your housing operates at peak efficiency and delivers consistent results.
Follow Manufacturer-Recommended Maintenance Schedules for Seals and Gaskets
Seals and gaskets are small components with a big impact. Neglecting their maintenance can lead to leaks, contamination, or system failure.
- Replace Seals Periodically: Even the best seals degrade over time. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended replacement schedule to ensure a tight, reliable seal. For example, in high-temperature applications, seals may need more frequent replacement due to thermal stress.
- Use Compatible Materials: Choose seals made from materials that are compatible with your application. For instance, EPDM works well for water filtration, while Viton is better suited for aggressive chemicals.
- Lubricate Seals: Apply a food-grade or chemical-compatible lubricant to seals during installation to prevent damage and ensure a proper fit.
By maintaining seals and gaskets, you protect your system from leaks and ensure consistent filtration performance.
Proper maintenance of stainless steel filter housings isn’t just about keeping them clean—it’s about preserving their integrity and ensuring they perform reliably in the long run. By following these tips, you can maximize the lifespan of your housings and maintain the efficiency of your filtration system.
FAQs: Quick Answers to Common Questions
Q: What’s the difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel?
A: The main difference lies in their composition and resistance to corrosion. 304 stainless steel contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel, making it suitable for general-purpose applications with low to moderate exposure to corrosive elements. 316 stainless steel, on the other hand, includes 2-3% molybdenum, which enhances its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. This makes 316 the better choice for harsh environments, such as those involving saltwater, acids, or aggressive chemicals.
Q: How often should filter housings be cleaned or maintained?
A: Clean and maintain filter housings based on your application and operating conditions. For most systems, inspect and clean housings during each filter change, which could range from weekly to quarterly depending on usage. In high-contaminant environments, clean housings more frequently to prevent buildup. Always follow the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Q: Can stainless steel filter housings handle seawater applications?
A: Yes, but you should use 316 stainless steel or a specialized alloy for seawater applications. The molybdenum content in 316 stainless steel provides superior resistance to chloride-induced corrosion, which is common in marine environments. For even harsher conditions, consider duplex stainless steel or Hastelloy for enhanced durability and corrosion resistance.
Q: What certifications are required for food-grade filter housings?
A: Food-grade filter housings should meet certifications such as FDA compliance for materials that come into contact with food. Additionally, 3-A Sanitary Standards ensure the housing meets hygiene requirements for dairy and other food processing applications. For international markets, look for certifications like EHEDG (European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group) to ensure compliance with global food safety standards.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Stainless steel filter housings offer unmatched durability, versatility across industries, and a hygienic design that meets the strictest standards. These qualities make them a reliable, long-term investment for even the most demanding applications. To ensure you select the best housing for your specific needs, consult with experts or trusted suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that align with your operational goals.




